-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
D.-A.A. Lamprou, L.G. van der Hem, A painless swelling of the abdominal wall, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2014, Issue 3, March 2014, rju011, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rju011
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Case report. A man with a painless swelling of the abdominal wall. A 77-year-old male presented with a progressively increasing painless swelling of the abdominal wall due to nodular fasciitis.
INTRODUCTION
A general physician refers a 77-year-old male with no previous illnesses to the department of surgery. At the time of presentation a subcostal swelling of the abdominal wall has been present for over 5 months. This painless swelling has progressively grown in size over the past few months.
CASE REPORT
On palpation the lesion is solid elastic to the touch. An ultrasound investigation with histological biopsy was made. Histological examination showed fibroma myxoid tissue with the suspicion on nodular fasciitis. Additional CAT-scan images (Fig. 1) revealed a smooth, oval and the peritoneum-bordered tumour located medially and spreading into the rectus abdominis muscle.
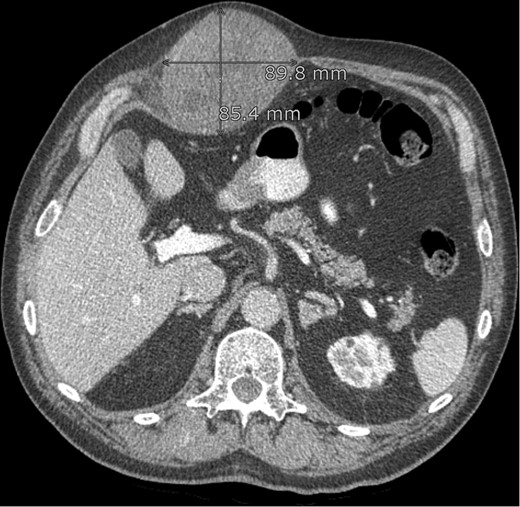
CT abdomen: lesion in the abdominal wall, possibly originating from the rectus abdominis muscle.
During surgery a large yellow lobular partially fibrotic mass (Fig. 2) was excised located entirely above the muscle fascia. Histological examination showed nodular fasciitis without signs of malignancy.
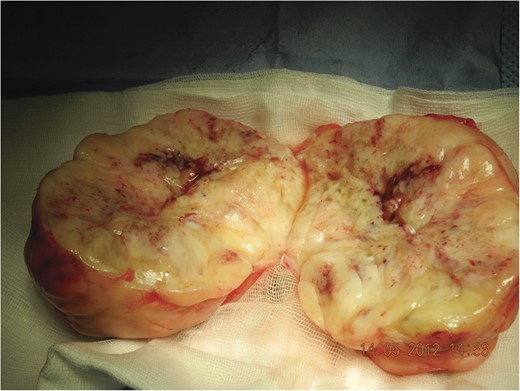
Tumour ex vivo, note the lobular structure with fibrous septa (incised).
DISCUSSION
Nodular fasciitis, also known as pseudosarcomatous fibromatosis, is predominately seen in young adults (20–40 years). Mostly affecting the upper extremities or trunk it can mimic a malignant sarcoma due to its rapid growth.



