-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Walter Colangeli, Valerio Facchini, Aleksandr Kapitonov, Marta Zappalà, Fabrizio Bozza, Roberto Becelli, Cystic lymphangioma in adult: a case report and a review of the literature, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2020, Issue 7, July 2020, rjaa179, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjaa179
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Cystic lymphangioma (CL) in adult is a very rare pathology. Its etiology remains unclear, but it is supposed to be congenital or to be a result of obstruction and lymph fluid retention of developing lymphatic vessels. It generally occurs in the head and neck region, probably because of the rich lymphatics in this area. It can be easily misdiagnosed with other cervicofacial masses. We present the case of a 56-year-old-female presented with a right-sided painless cervical swelling. Ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging were performed and a surgical complete removal was carried out. Histological examination revealed that the mass was composed by a variety of dilated lymph vessels involved in a fibrovascular stroma. Diagnose of CL was done. With this article, we want to highlight the features of CL and its role in the differential diagnoses of adults’ cervicofacial masses.
INTRODUCTION
Cystic lymphangioma (CL) is a benign congenital lymphatic malformation [1]. Children under 2 years of age are mostly affected. In adults, it is rarely seen [2].
Head and neck (HN) is the mainly affected region and symptoms due to local compression can occur related to the location and the size of the tumor [3].
CL should be included in differential diagnoses with other adult’s cervicofacial masses.
In this article, a rare case of CL initially misdiagnosed with a branchial cleft cyst is presented.
The aim of this article is to highlight the role of this rare entity in the differential diagnosis of cervicofacial masses in adults.
CASE PRESENTATION
A 56-year-old female without personal and familiar history of tumors presented to our department on September 2018 with a right-sided painless cervical swelling. Tumor onset was referred to be 7 months before she came to our attention. The mass presented with a progressively enlargement. Neither history of trauma nor recent upper respiratory tract infections were referred. Compressive symptoms were not also referred.
On physical examination, the mass was located in the right submandibular region. Skin overlying the mass was not compromised. It was soft to tender in consistency, lobular with ill-defined margins, painless and freely movable, and cervical lymphadenopathy was not clinically detected (Fig. 1). Normal function of the facial nerve was observed. No alteration of the lingual nerve sensitivity was referred.
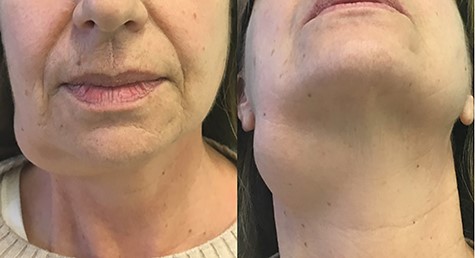
Ultrasonography (US) revealed a cervical anechoic multilobulated mass in the submandibular space.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed and showed a cystic mass of 4 × 4 × 3.5 cm in size located under the right mandible and strictly adherent to the submandibular gland. On T2-weighted images, the mass resulted hyperintense, while hypointense in those T1 weighted (Fig. 2).
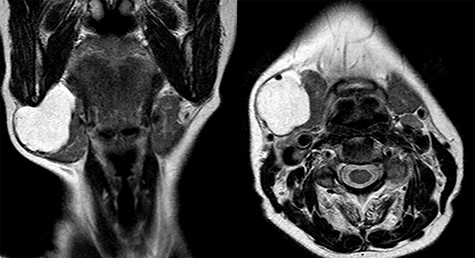
A branchial cleft cyst was firstly supposed.
Surgery was performed under general anesthesia. Horizontal incision was made about two fingers below the mandible in order to avoid marginalis mandibulae nerve injury. The mass was cleaved from the submandibular gland and completely removed, and then the surgical specimen was sent for histopathological examination.
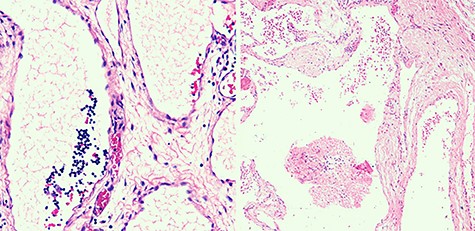
Macroscopically, cysts bigger than 2 cm3 were observed. Microscopically, the mass was composed by a variety of dilated lymph vessels involved in a fibrovascular stroma (Fig. 3). Diagnose of completely excised CL was done.
No facial nerve injury was noticed after surgery.
A follow-up was programmed. At the date, after 18 months from surgery, no relapses were noticed.
DISCUSSION
CL, also called cystic hygroma (CH) or better macrocystic lymphatic malformation (LM), is a benign congenital LM [1].
Children under 2 years of age are mainly affected (80–90%) with a 1.2–2.8 per 100 000 incidence rate [4]. Adults are instead rarely affected [2]. Precise etiology remains unclear but it is supposed to be congenital or to be a result of obstruction and lymph fluid retention of developing lymphatic vessels caused by certain acquired factors [4, 5]. Infection, trauma (included surgery) and neoplasms are considered as more common causes. It has no gender predilection [1].
It can develop in every part of the body, but mostly occur in HN region, followed by clavicle and axillary regions, probably because of rich lymphatics in this area [3].
Over years, LMs have been classified by several classification systems. In 1843, Wernher divided LMs into three types: capillary, cavernous and cystic. In 1989, Kennedy [1] described four different types: superficial cutaneous, cavernous, CH and diffuse systematic. In 1993, McGill et al. [5] proposed a classification based on computed tomography (CT) scan, anatomical sites and histology: Type 1 are macrocystic and below mylohyoid muscle involving anterior and posterior triangles of the neck and Type 2 are microcystic and above mylohyoid muscle involving lip, tongue and oral cavity. In 1995, based on the location and on the extension of the mass, De Serres et al. [6] proposed a staging system: unilateral infrahyoid, suprahyoid, infra- and suprahyoid, bilateral infrahyoid and infra- and suprahyoid. In 1996, Smith et al. [7] described LMs as macrocystic (containing cysts >2 cm in diameter), microcystic and mixed variant.
On clinical examination, CL is usually asymptomatic. Otherwise, extensive masses can lead to compressive symptoms related to location, size and growing rate. The more encountered symptoms are dysphagia and dyspnea due to the compression of respectively esophagus and trachea or larynx [1, 5].
On patient evaluation, various diagnostic hypotheses should be considered such as lipoma, branchial cleft cyst, thyroglossal duct cyst, tumors of major salivary gland, hematoma, carotid body tumors, soft tissue sarcomas and thyroid masses.
On physical examination, CL may be different in size and can develop in every locations of HN region. It usually appears as a soft, non-tender, painless, lobular with unlimited mobility mass.
Assessment methods include US, CT scan and MRI. US examination should be performed as first imaging approach and it usually shows an anechoic multilobulated cystic mass. A CT scan or better a MRI may be performed in order to do a most accurate presurgery evaluation. On MRI, T1-weighted images show an isointense signal and T2-weighted images show a hyperintense signal without contrast enhancement.
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is still debated due to the increased risk of infection, bleeding and recurrence [8]. In our opinion, it has a low diagnostic value because it does not modify our treatment approach.
Although, in adults, a definitive diagnosis is based on histopathological examination.
Sclerotherapy and laser therapy are alternative techniques used as first approach in children but just as adjuvant therapies in selected adult cases [2]. Considering the possibility of spontaneous resolution, watchful wait has also been suggested from Kennedy et al. [9] for selected cases, avoiding risks of surgery, which include facial nerve palsy, seroma, heavy bleeding, infection and great tissue defects [4]. In our opinion, surgical complete removal of the mass should be considered as the only definitive treatment of CL in adults.
CL has a recurrence rate of ~10–15% if not completely surgically excised. Recurrence is also related to location of the lesion over/under hyoid bone and presence/absence of a well-defined capsule [10].
In conclusion, by presenting our case, we want to underline the rarity of CL in adults and its role in the differential diagnoses for HN masses in adults.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
Authors report no conflict of interest.



