-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Rachel Martin, Winn Mathews, Steven Scarcliff, A rare presentation of breast cancer: near obstructing rectal mass and gastric outlet obstruction, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2016, Issue 9, September 2016, rjw162, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjw162
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Breast cancer metastasizes to the gastrointestinal (GI) tract are exceedingly rare. The low incidence and vague presentation of GI metastasizes often cause delay in diagnosis and treatment. Here, we present a case of metastatic breast cancer causing gastric outlet obstruction and rectal obstruction.
Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common noncutaneous cancer diagnosed in women and is the second most common cause of cancer death in women worldwide. Approximately 5% of women in the USA with breast cancer have stage IV disease at time of diagnosis. The most common sites of breast cancer metastasis include lungs, liver, bone and brain [1]. GI metastases are rare and often occur years after breast cancer diagnosis. The low incidence and vague symptoms of these metastases can create a diagnostic challenge and delay treatment. We report a rare and unusual case of metastatic mammary carcinoma presenting as gastric outlet obstruction and near obstructing rectal mass.
Case Report
A 61-year-old African American female presented to her primary care provider with a 1-month history of nausea, emesis, constipation and 20 pound weight loss. She also reported superficial skin changes on bilateral breasts and a palpable mass in her left breast. Mammography revealed a hypoechoic lesion of the left breast and overlying asymmetry classified as BIRADS 4C which was not present on the patient's annual mammogram 8 months prior. The patient was referred to general surgery for biopsies of the left breast mass, overlying skin of both breasts and an axillary skin lesion. Pathology report of all lesions was ER(−), Her2/neu(−), GATA3(+) poorly differentiated mammary carcinoma. Computed Tomography (CT) scan of chest, abdomen and pelvis was performed for cancer staging. The scan revealed multiple osteoblastic metastasis within the sternum and spine, circumferential rectosigmoid mural thickening and duodenal bulb wall thickening (Fig. 1). The duodenal and rectal lesions were further evaluated with endoscopy. On upper endoscopy there was extrinsic compression of the antrum and stenosis of the pylorus and duodenal bulb. On colonoscopy, there was firm, friable, erythematous stricture circumferentially in the distal 5 cm of rectum (Fig. 2). Pathologic evaluation of the duodenal and rectal lesions revealed poorly differentiated carcinoma consistent with mammary primary (Fig. 3).
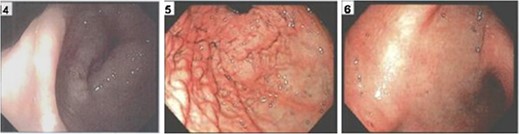
Rectal stricture (left), external compression of antrum (middle), duodenal bulb wall thickening (right).
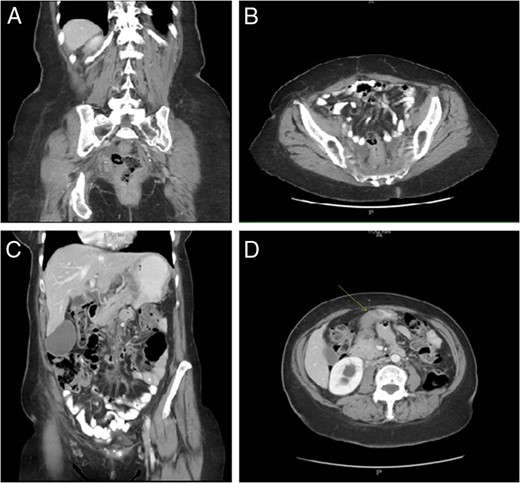
Circumferential rectosigmoid mural thickening (A, B); Duodenal bulb wall thickening (C, D).
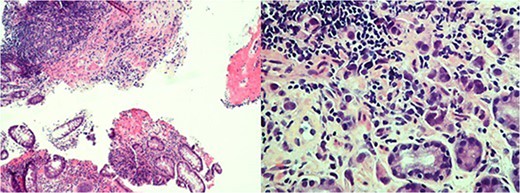
Rectal mass biopsy with atypical submucosal infiltrate with stains indicative of poorly differentiated carcinoma with breast primary (left); Gastric mucosa biopsy with poorly differentiated malignant large cell neoplasm, stains consistent with metastatic breast adenocarcinoma (right).
Discussion
GI metastases from breast cancer are rare with large series noting an incidence <1% [2]. The most common site of GI tract involvement is the stomach, followed by small bowel and colon. Rectal metastases are exceedingly rare, comprising 4% of all GI metastases. While these metastatic tumors are rare, autopsy series have revealed that many breast cancer patients have GI metastases that will remain clinically occult [3].
Clinical manifestations are usually nausea, vomiting and vague abdominal discomfort mimicking primary GI malignancies, gastroenteritis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. These nonspecific symptoms, as well as presentation frequently occurring 5–7 years after initial breast cancer diagnosis, makes the diagnosis of a GI metastasis difficult. Even less common, and often more difficult to diagnose, is a breast cancer initially presenting as a GI metastasis [4].
Radiologic and endoscopic evaluation can be used at initial presentation; however, histologic evaluation of the GI mass is needed to differentiate metastatic breast cancer and a primary GI malignancy. CT scan, when performed, can localize the mass but is nonspecific in diagnosis. Endoscopic appearance of a GI metastatic lesion frequently is that of linitis plastica. Instead of a discrete mass there is often a circumferential stricture and discrete wall thickening.
Histopathological diagnosis can be difficult as biopsies obtained during endoscopy will many times not reveal malignant cells. Breast cancer metastases often appear in the submucosa or muscularis propria as small nests of tumor cells, therefore biopsies should be multiple and deep. Abnormal glands surrounded by normal glands helps to differentiate primary GI malignancy and breast cancer metastases [5]. Immunohistochemical analysis may be the most consistent way of differentiating metastatic and primary GI malignancy. Though lobular histology comprises only 20% of breast cancers, it represents the most common type metastasizing to the GI tract [1].
Minimally invasive interventions such as endoscopic stents, dilations and bowel regimens along with systemic chemotherapy are the preferred management of GI metastases as resection and palliative surgery has not been shown to affect overall survival. Surgery may be indicated in rare cases of obstruction but should be limited to palliative bypasses or diverting ostomies.



