-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Andrea Lanaia, Maurizio Zizzo, Concetto M. Cartelli, Matteo Fumagalli, Stefano Bonilauri, Laparoscopic removal of gastric band after laparoscopic gastric bypass and following placement of adjustable gastric band, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2015, Issue 8, August 2015, rjv095, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjv095
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Banded gastric bypass is a bariatric surgical intervention that has been regularly performed in many centers. According to some series, banded gastric bypass is safe and feasible. We describe the case of a 42-year-old woman undergoing laparoscopic gastric bypass in 2008. Subsequently, she underwent surgery in order to place adjustable gastric banding on previous bypass because of gastric pouch dilatation. Five months later, patient showed anorexia and signs of malnutrition. For this reason, she underwent laparoscopic removal of gastric banding. In our opinion, placing a device to restrict an already dilated gastric pouch must be avoided.
INTRODUCTION
Banded gastric bypass is a bariatric surgical intervention that has been regularly performed in many centers. The theoretical advantage is that of reducing the rate of drawbacks occurring after gastric bypass, namely gastric pouch dilatation [1–3]. According to some series, banded gastric bypass is safe and feasible, because it has a low risk of complications such as band displacement or gastric pouch erosion [2, 3]. We describe the case of a 42-year-old woman undergoing laparoscopic gastric bypass in 2008, because of morbid obesity. After an initial weight loss, the patient started to regain weight because of gastric pouch dilatation. For this reason, in 2013, she underwent surgery in order to place adjustable gastric banding on previous bypass. Five months later, patient showed symptoms such as anorexia, dysphagia for solids and fluids, nausea, vomiting, signs of malnutrition with dysproteinemia, hypoalbuminemia and ankle swelling.
CASE REPORT
On the first day of admission, gastric banding was completely deflated. Rx abdomen showed posterior slippage of the ring (Fig. 1). Subsequently, the patient underwent rehydration therapy, 20-day total parenteral nutrition and infusion of human albumin. During that period, we examined her upper digestive tract with oral water-soluble contrast (Fig. 2) with the result of a thin liquid passage downstream of the ring and marked gastric pouch distension. Esofagogastroscopy was performed, which was negative for erosion or gastric perforation; however, it revealed a 1-cm-diameter passage through the gastric band. Despite an improvement in symptoms with partial resumption of semi-liquid intake, the patient continued to experience nausea and vomiting. For this reason, she underwent laparoscopic removal of gastric banding. In the operating room, she was placed in the lithotomy position; we placed a 10-mm optical trocar in supraumbilical region, a 5-mm one in the right upper quadrant and a 10-mm one in left upper quadrant near the subcutaneous tank. After lysis of adhesions between liver and stomach, the intraoperative picture showed a banding displacement, confirming posterior slippage of the banding and its sliding back to the level of previous gastro-jejunal anastomosis. Ascitic effusion due to dysproteinemia was reported. A methylene blue test showed no gastric perforation. After this procedure, the patient started to resume liquid intake in the first postoperative day and food intake in the second postoperative day, with complete resolution of vomiting and nausea. Then, she was discharged with the advice of an appropriate diet and invited to attend a recall visit 10 days later. In subsequent follow-up, the complete resolution of clinical symptoms was confirmed together with an improvement of the biohumoral picture.
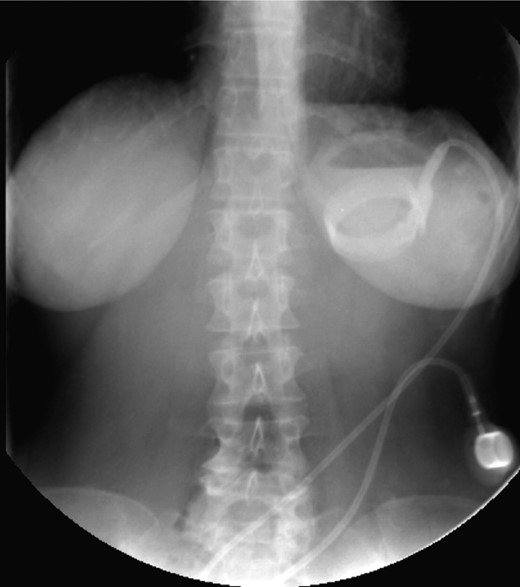
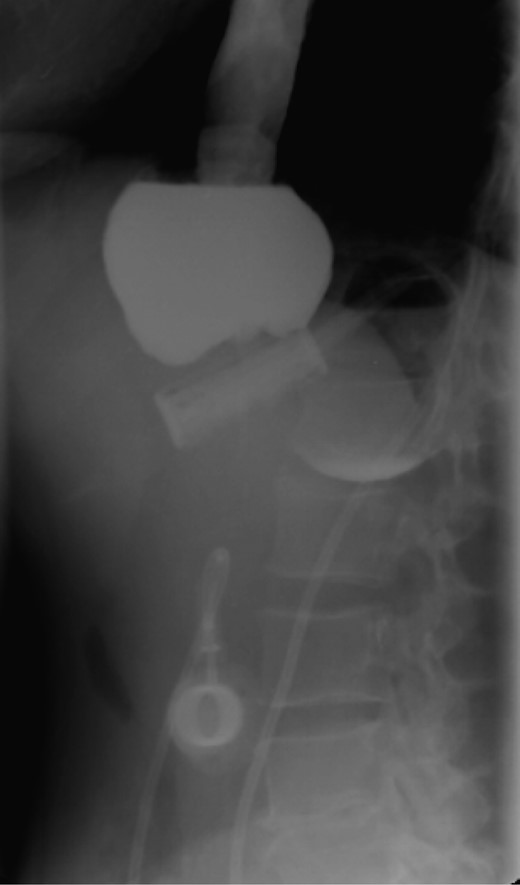
Water-soluble contrast shows a thin liquid passage downstream of the ring and marked gastric pouch distension.
DISCUSSION
Many case studies universally acknowledge banded gastric bypass as a safe and effective procedure. However, complications can be very serious [4–6]. There is no doubt that patient must be made aware of the risks of such intervention and, last but not least, patient must undergo a close postoperative follow-up. In our opinion, however, placing a device to restrict an already dilated gastric pouch must be avoided; rather, it would be useful to prevent this occurrence by educating patients to follow a correct diet.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
None declared.



