-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Syed Sohail Ahmad, Kaleem Khalilullah, Katherine McGowan, Katrina Dillon, Unexpected destination! Rectal carcinoma metastasis to breast, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2019, Issue 3, March 2019, rjz036, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjz036
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Rectal cancer metastasis to the breast is rare with around 19 cases reported in literature. It signifies diffuse disseminated disease or highly aggressive tumour, such that surgical intervention other than palliation has a limited role. We report a case of a 43-year-old with the above presentation. As the management differs and because of its rarity the importance of the diagnosis between primary and the metastatic breast cancer is imperative.
INTRODUCTION
Nineteen percent of patients newly diagnosed with colorectal cancer present with distant metastasis at the time of diagnosis and patients treated for cure develop metastatic disease in nearly 40%. Metastases from rectal cancer to multiple organs have been reported either as synchronous or metachronous lesions [1]. Regardless, metastatic disease from the rectum to unusual sites carries substantially poor prognosis.
CASE REPORT
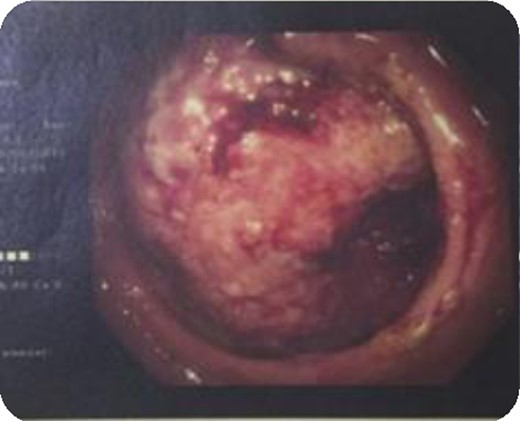
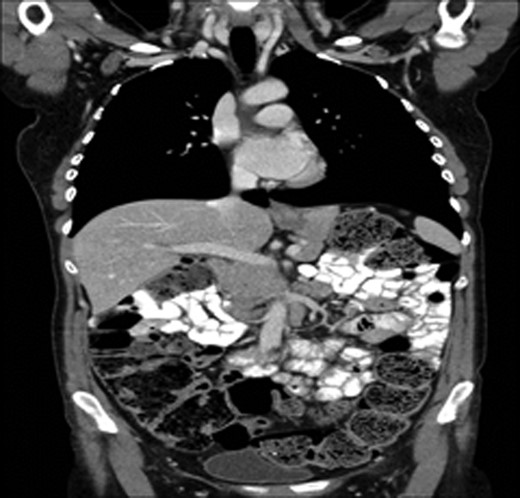
A 43-year-old female, 10 weeks postpartum, underwent colonoscopy for bleeding per rectum showing a bulky tumour (Fig. 1) in the rectum at 5 cm. Histologically poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the rectum (Fig. 2) T3N1Mo. Underwent laparoscopic loop ileostomy formation for impending bowel obstruction. Bloods showed Hemoglobin13.6 g/dL, Bilirubin 10umol/L, CEA 3.6 ng/mL. MRI pelvis (Fig. 3a and b) showed locally advanced annular neoplasm of mid and upper rectum. CT TAP (Fig. 4) reported no distant metastasis. She had neoadjuvant chemoradiothreapy with poor response. Post chemotherapy she noticed a lump in her right breast and axilla. Breast mammogram (Fig. 5a) showed 26 mm lesion in the right breast at 10 o'clock position and ultrasound showed 27 mm lesion in right axilla. Core biopsy (Fig. 6) reported signet ring morphology. The tumour stained positive with CK20, CDX-2 and CEA. There was no staining with CK7, ER, PR or Her-2. The rectal biopsy specimen, also analysed for KRAS status, was KRAS/NRAS/BRAF negative. She is being followed up by oncology with FOLFOX+Panitumumab.
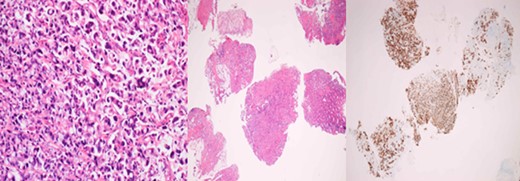
Primary rectal biopsy showing mucinous poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with signet cells KRAS/BRAS/NRAF negative.
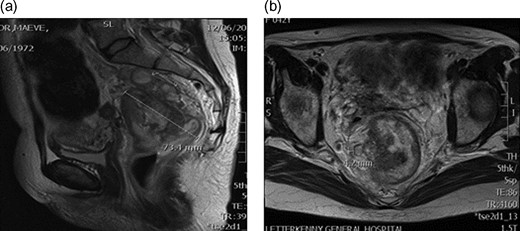
(a) MRI pelvis showing rectal tumour 7.3 cm two lymph nodes. (b) MRI pelvis Mucinous component within 5 mm of the right meso-rectum.
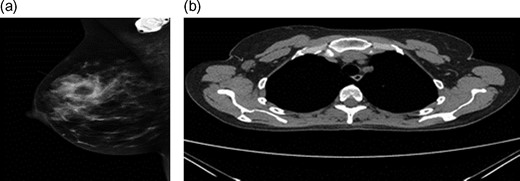
(a) Mammogram post-neoadjuvant chemoradiothreapy showing right breast mass. (b) CT TAP pos-tneoadjuvant chemoradiothreapy showing enlarged right axillary lymph node.
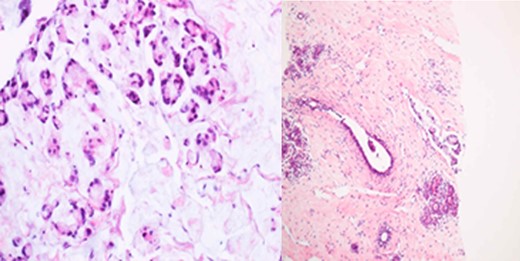
Breast core biopsy showing features similar to the primary rectal cancer.
DISCUSSION
Most breast metastases originate from the contra lateral breast [2]. Metastases to the breast from extra-mammary malignancies are rare 0.43%. Lymphoma, melanoma, sarcoma, lung carcinoma and ovarian tumour are common extra-mammary primary malignancies metastasizing to breast. Metastases from colon to breast was first reported by McIntosh and from rectum by Lal in 1999 [3]. A handful of cases of CRC metastasis to the breast have been reported, with two largest studies presenting two new cases each [4].
These metastatic lesions must be differentiated from primary breast tumours on the basis of history, clinical, radiological features, morphology of tumour and immune-histochemistry [5]. Most metastases present as palpable breast masses, occasionally adherent to the skin with slight left predominance, most common being upper outer quadrant. Rarely are there multiple or bilateral lesions [4]. Schaekelford et al. reported 55% to the left, 30% to the right and only 3% with bilateral breast metastasis. Toombs and Kalisher reported pain, tenderness or discharge is distinctly unusual. Nipple retraction has not been described, although adherence to the skin has been reported in 25%. Axillary node involvement was frequently encountered. Rumana, Rakesh Kumar, Ruiz, et al. [6, 7] reported cases of bilateral breast metastasis in young patients. Suganthi Krishnamurthy reported the youngest patient age 23 years old with rectal cancer metastasis to the breast. Hisham et al. [2] reported an unusual case of rectal carcinoma metastasis to the breast along with ocular involvement. Mihai et al. [8] reported a 53-year-old woman who post chemotherapy developed breast metastasis and later cutaneous metastasis similar in disease progression to our patient (Table 1).
| References . | Age . | Sex . | Primary cancer . | Metastasis . | Location of breast metastasis . | Radiology . | Histology . | Management . | OPD . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| My patient | 43 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast | Rt upper quadrant/rt axilla | MRI/CT TAP/Mammogram/US | Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma | Chemoradiothreapy,oncology follow-up | Oncology |
| Lal and Joffe [3] | 69 | F | Rectal cancerT3N2R0Mo | Breast, liver, lung, brain, skin | Left upper outer quadrant | CT TAP, FNA, wide local excision, elevated CEA, CA19.9 | Moderately differentiated mucin secreting adenocarcinoma breast histology moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma, ER negative | Radical anterior resectional wide local excision Poor response to chemotherapy | RIP 4/12 after breast diagnosis |
| Sanchez et al. [1] | 36 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast metastasis | Left outer upper quadrant 6 cm in size | ||||
| Hisham et al. [2] | 32 | F | Rectal cancer | 10 months after APR, breast, spine, left eye, orbit | Left breast metastasis | Colonoscopy, CT abdomenpelvis Lumbosacral x-ray, MRI brain | Poorly differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma of the rectum, Breast Bx similar | APR and total mesorectal excision, excision of posterior vaginal wall, cuff of the tissue in the lateral pelvic wall | RIP 2/12 |
| Mihai et al. [8] | 53 | F | Rectal cancer | Lung, breast metastasis, skin metastasis | Breast lump | Ultrasound, mammogram, FNA, core biopsies, local excision | Chemothreapy, local excision, Post op chemothreapy | RIP | |
| Wakeham et al. [4] | 43 | F | Rectal Cancer | Bilateral breast | Breast lump 2×2.2 cm2 | Dukes C rectal cancer | |||
| Li et al. [5] | 51 | F | Perforated rectal cancer | Breast, lung, soft tissue | 3 cm mass in the right upper quadrant | CT abdomen pelvis,Mammogram,US breast,axilla | Invasive poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma rectal carcinoma T4N0M0, Core Bx breast and axilla triple negative similar to rectal histology | Laparotomy colostomy, preop radichemothreapy | RIP 12 months |
| Rumana Makhdomi [6] | 28 | F | Rectal cancer 4 cm away from anal verge | Bilateral breast metastasis | Largest 3×2 cm2 and smallest 2×1 cm2 | Sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, contrast enhanced computed tomography, mamamography, FNAC | Mucus secreting adenocarcinoma with signet-ring differentiation, metastatic mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast,ER/PR negative | Anteroperineal resection, adjuvant chemothreapy | OPD follow up |
| Singh et al. [10] | 42 | F | Rectal cancerT4 N1M0 | Right Breast lump | Outer upper quadrant 5×4 cm2 | Mammogram, FNAC, pleural fluid cytology, core needle biopsy, CEA mildly elevated | Mucin secreting adenocarcinoma with signet ring cell Signet cell carcinoma CK20 positive, CK7, ER/PR negative | Anterior resection, chemoradiation, chemothreapy | RIP 2/12 after breast metastasis |
| Hasukic et al. [9] | 63 | F | Rectal cancer T3N1M0 | Right breast mass 3×2 cm | Right upper outer quadrant | Mammography, Ultrasound | Rectal adenocarcinoma T3N1M0, breast biopsy, Adenocarcinoma ER/PR neg | APR, Adjuvant chemoradiothreapy, open excisional breast biopsy | RIP post 4/12 breast pathology |
| Ruiz et al. [7] | 36 | F | Rectal cancer | Bilateral breast left axilla right groin | Bilateral breast | CT abdomen pelvis, Mammogram Ultrasound | Poorly differentiated rectal carcinoma with signet ring cellT3N1M0 | APR with hysterectomy, adjuvant radiochemotherapy exploratory laparotomy, incisional bx of both breast, chemothreapy nine cycles | RIP 6 /12 after breast mets diagnosis |
| Ting Wang et al. [11] | 38 | M | Rectal cancer | Right mammary mass 7 years after surgery | Anterior resection, core needle bx, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, modified radical mastectomy | ||||
| Suganthi Krishnamurthy et al. [12] | 23 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast/axillary metastasis two 1/2 months later | Right upper outer quadrant | Colonoscopy, CT TAP, FNAC, Core Bx | Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with signet cell | Emergency laparotomy, loop colostomy, palliative chemotherapy |
| References . | Age . | Sex . | Primary cancer . | Metastasis . | Location of breast metastasis . | Radiology . | Histology . | Management . | OPD . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| My patient | 43 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast | Rt upper quadrant/rt axilla | MRI/CT TAP/Mammogram/US | Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma | Chemoradiothreapy,oncology follow-up | Oncology |
| Lal and Joffe [3] | 69 | F | Rectal cancerT3N2R0Mo | Breast, liver, lung, brain, skin | Left upper outer quadrant | CT TAP, FNA, wide local excision, elevated CEA, CA19.9 | Moderately differentiated mucin secreting adenocarcinoma breast histology moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma, ER negative | Radical anterior resectional wide local excision Poor response to chemotherapy | RIP 4/12 after breast diagnosis |
| Sanchez et al. [1] | 36 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast metastasis | Left outer upper quadrant 6 cm in size | ||||
| Hisham et al. [2] | 32 | F | Rectal cancer | 10 months after APR, breast, spine, left eye, orbit | Left breast metastasis | Colonoscopy, CT abdomenpelvis Lumbosacral x-ray, MRI brain | Poorly differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma of the rectum, Breast Bx similar | APR and total mesorectal excision, excision of posterior vaginal wall, cuff of the tissue in the lateral pelvic wall | RIP 2/12 |
| Mihai et al. [8] | 53 | F | Rectal cancer | Lung, breast metastasis, skin metastasis | Breast lump | Ultrasound, mammogram, FNA, core biopsies, local excision | Chemothreapy, local excision, Post op chemothreapy | RIP | |
| Wakeham et al. [4] | 43 | F | Rectal Cancer | Bilateral breast | Breast lump 2×2.2 cm2 | Dukes C rectal cancer | |||
| Li et al. [5] | 51 | F | Perforated rectal cancer | Breast, lung, soft tissue | 3 cm mass in the right upper quadrant | CT abdomen pelvis,Mammogram,US breast,axilla | Invasive poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma rectal carcinoma T4N0M0, Core Bx breast and axilla triple negative similar to rectal histology | Laparotomy colostomy, preop radichemothreapy | RIP 12 months |
| Rumana Makhdomi [6] | 28 | F | Rectal cancer 4 cm away from anal verge | Bilateral breast metastasis | Largest 3×2 cm2 and smallest 2×1 cm2 | Sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, contrast enhanced computed tomography, mamamography, FNAC | Mucus secreting adenocarcinoma with signet-ring differentiation, metastatic mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast,ER/PR negative | Anteroperineal resection, adjuvant chemothreapy | OPD follow up |
| Singh et al. [10] | 42 | F | Rectal cancerT4 N1M0 | Right Breast lump | Outer upper quadrant 5×4 cm2 | Mammogram, FNAC, pleural fluid cytology, core needle biopsy, CEA mildly elevated | Mucin secreting adenocarcinoma with signet ring cell Signet cell carcinoma CK20 positive, CK7, ER/PR negative | Anterior resection, chemoradiation, chemothreapy | RIP 2/12 after breast metastasis |
| Hasukic et al. [9] | 63 | F | Rectal cancer T3N1M0 | Right breast mass 3×2 cm | Right upper outer quadrant | Mammography, Ultrasound | Rectal adenocarcinoma T3N1M0, breast biopsy, Adenocarcinoma ER/PR neg | APR, Adjuvant chemoradiothreapy, open excisional breast biopsy | RIP post 4/12 breast pathology |
| Ruiz et al. [7] | 36 | F | Rectal cancer | Bilateral breast left axilla right groin | Bilateral breast | CT abdomen pelvis, Mammogram Ultrasound | Poorly differentiated rectal carcinoma with signet ring cellT3N1M0 | APR with hysterectomy, adjuvant radiochemotherapy exploratory laparotomy, incisional bx of both breast, chemothreapy nine cycles | RIP 6 /12 after breast mets diagnosis |
| Ting Wang et al. [11] | 38 | M | Rectal cancer | Right mammary mass 7 years after surgery | Anterior resection, core needle bx, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, modified radical mastectomy | ||||
| Suganthi Krishnamurthy et al. [12] | 23 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast/axillary metastasis two 1/2 months later | Right upper outer quadrant | Colonoscopy, CT TAP, FNAC, Core Bx | Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with signet cell | Emergency laparotomy, loop colostomy, palliative chemotherapy |
| References . | Age . | Sex . | Primary cancer . | Metastasis . | Location of breast metastasis . | Radiology . | Histology . | Management . | OPD . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| My patient | 43 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast | Rt upper quadrant/rt axilla | MRI/CT TAP/Mammogram/US | Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma | Chemoradiothreapy,oncology follow-up | Oncology |
| Lal and Joffe [3] | 69 | F | Rectal cancerT3N2R0Mo | Breast, liver, lung, brain, skin | Left upper outer quadrant | CT TAP, FNA, wide local excision, elevated CEA, CA19.9 | Moderately differentiated mucin secreting adenocarcinoma breast histology moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma, ER negative | Radical anterior resectional wide local excision Poor response to chemotherapy | RIP 4/12 after breast diagnosis |
| Sanchez et al. [1] | 36 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast metastasis | Left outer upper quadrant 6 cm in size | ||||
| Hisham et al. [2] | 32 | F | Rectal cancer | 10 months after APR, breast, spine, left eye, orbit | Left breast metastasis | Colonoscopy, CT abdomenpelvis Lumbosacral x-ray, MRI brain | Poorly differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma of the rectum, Breast Bx similar | APR and total mesorectal excision, excision of posterior vaginal wall, cuff of the tissue in the lateral pelvic wall | RIP 2/12 |
| Mihai et al. [8] | 53 | F | Rectal cancer | Lung, breast metastasis, skin metastasis | Breast lump | Ultrasound, mammogram, FNA, core biopsies, local excision | Chemothreapy, local excision, Post op chemothreapy | RIP | |
| Wakeham et al. [4] | 43 | F | Rectal Cancer | Bilateral breast | Breast lump 2×2.2 cm2 | Dukes C rectal cancer | |||
| Li et al. [5] | 51 | F | Perforated rectal cancer | Breast, lung, soft tissue | 3 cm mass in the right upper quadrant | CT abdomen pelvis,Mammogram,US breast,axilla | Invasive poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma rectal carcinoma T4N0M0, Core Bx breast and axilla triple negative similar to rectal histology | Laparotomy colostomy, preop radichemothreapy | RIP 12 months |
| Rumana Makhdomi [6] | 28 | F | Rectal cancer 4 cm away from anal verge | Bilateral breast metastasis | Largest 3×2 cm2 and smallest 2×1 cm2 | Sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, contrast enhanced computed tomography, mamamography, FNAC | Mucus secreting adenocarcinoma with signet-ring differentiation, metastatic mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast,ER/PR negative | Anteroperineal resection, adjuvant chemothreapy | OPD follow up |
| Singh et al. [10] | 42 | F | Rectal cancerT4 N1M0 | Right Breast lump | Outer upper quadrant 5×4 cm2 | Mammogram, FNAC, pleural fluid cytology, core needle biopsy, CEA mildly elevated | Mucin secreting adenocarcinoma with signet ring cell Signet cell carcinoma CK20 positive, CK7, ER/PR negative | Anterior resection, chemoradiation, chemothreapy | RIP 2/12 after breast metastasis |
| Hasukic et al. [9] | 63 | F | Rectal cancer T3N1M0 | Right breast mass 3×2 cm | Right upper outer quadrant | Mammography, Ultrasound | Rectal adenocarcinoma T3N1M0, breast biopsy, Adenocarcinoma ER/PR neg | APR, Adjuvant chemoradiothreapy, open excisional breast biopsy | RIP post 4/12 breast pathology |
| Ruiz et al. [7] | 36 | F | Rectal cancer | Bilateral breast left axilla right groin | Bilateral breast | CT abdomen pelvis, Mammogram Ultrasound | Poorly differentiated rectal carcinoma with signet ring cellT3N1M0 | APR with hysterectomy, adjuvant radiochemotherapy exploratory laparotomy, incisional bx of both breast, chemothreapy nine cycles | RIP 6 /12 after breast mets diagnosis |
| Ting Wang et al. [11] | 38 | M | Rectal cancer | Right mammary mass 7 years after surgery | Anterior resection, core needle bx, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, modified radical mastectomy | ||||
| Suganthi Krishnamurthy et al. [12] | 23 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast/axillary metastasis two 1/2 months later | Right upper outer quadrant | Colonoscopy, CT TAP, FNAC, Core Bx | Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with signet cell | Emergency laparotomy, loop colostomy, palliative chemotherapy |
| References . | Age . | Sex . | Primary cancer . | Metastasis . | Location of breast metastasis . | Radiology . | Histology . | Management . | OPD . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| My patient | 43 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast | Rt upper quadrant/rt axilla | MRI/CT TAP/Mammogram/US | Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma | Chemoradiothreapy,oncology follow-up | Oncology |
| Lal and Joffe [3] | 69 | F | Rectal cancerT3N2R0Mo | Breast, liver, lung, brain, skin | Left upper outer quadrant | CT TAP, FNA, wide local excision, elevated CEA, CA19.9 | Moderately differentiated mucin secreting adenocarcinoma breast histology moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma, ER negative | Radical anterior resectional wide local excision Poor response to chemotherapy | RIP 4/12 after breast diagnosis |
| Sanchez et al. [1] | 36 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast metastasis | Left outer upper quadrant 6 cm in size | ||||
| Hisham et al. [2] | 32 | F | Rectal cancer | 10 months after APR, breast, spine, left eye, orbit | Left breast metastasis | Colonoscopy, CT abdomenpelvis Lumbosacral x-ray, MRI brain | Poorly differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma of the rectum, Breast Bx similar | APR and total mesorectal excision, excision of posterior vaginal wall, cuff of the tissue in the lateral pelvic wall | RIP 2/12 |
| Mihai et al. [8] | 53 | F | Rectal cancer | Lung, breast metastasis, skin metastasis | Breast lump | Ultrasound, mammogram, FNA, core biopsies, local excision | Chemothreapy, local excision, Post op chemothreapy | RIP | |
| Wakeham et al. [4] | 43 | F | Rectal Cancer | Bilateral breast | Breast lump 2×2.2 cm2 | Dukes C rectal cancer | |||
| Li et al. [5] | 51 | F | Perforated rectal cancer | Breast, lung, soft tissue | 3 cm mass in the right upper quadrant | CT abdomen pelvis,Mammogram,US breast,axilla | Invasive poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma rectal carcinoma T4N0M0, Core Bx breast and axilla triple negative similar to rectal histology | Laparotomy colostomy, preop radichemothreapy | RIP 12 months |
| Rumana Makhdomi [6] | 28 | F | Rectal cancer 4 cm away from anal verge | Bilateral breast metastasis | Largest 3×2 cm2 and smallest 2×1 cm2 | Sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, contrast enhanced computed tomography, mamamography, FNAC | Mucus secreting adenocarcinoma with signet-ring differentiation, metastatic mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast,ER/PR negative | Anteroperineal resection, adjuvant chemothreapy | OPD follow up |
| Singh et al. [10] | 42 | F | Rectal cancerT4 N1M0 | Right Breast lump | Outer upper quadrant 5×4 cm2 | Mammogram, FNAC, pleural fluid cytology, core needle biopsy, CEA mildly elevated | Mucin secreting adenocarcinoma with signet ring cell Signet cell carcinoma CK20 positive, CK7, ER/PR negative | Anterior resection, chemoradiation, chemothreapy | RIP 2/12 after breast metastasis |
| Hasukic et al. [9] | 63 | F | Rectal cancer T3N1M0 | Right breast mass 3×2 cm | Right upper outer quadrant | Mammography, Ultrasound | Rectal adenocarcinoma T3N1M0, breast biopsy, Adenocarcinoma ER/PR neg | APR, Adjuvant chemoradiothreapy, open excisional breast biopsy | RIP post 4/12 breast pathology |
| Ruiz et al. [7] | 36 | F | Rectal cancer | Bilateral breast left axilla right groin | Bilateral breast | CT abdomen pelvis, Mammogram Ultrasound | Poorly differentiated rectal carcinoma with signet ring cellT3N1M0 | APR with hysterectomy, adjuvant radiochemotherapy exploratory laparotomy, incisional bx of both breast, chemothreapy nine cycles | RIP 6 /12 after breast mets diagnosis |
| Ting Wang et al. [11] | 38 | M | Rectal cancer | Right mammary mass 7 years after surgery | Anterior resection, core needle bx, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, modified radical mastectomy | ||||
| Suganthi Krishnamurthy et al. [12] | 23 | F | Rectal cancer | Breast/axillary metastasis two 1/2 months later | Right upper outer quadrant | Colonoscopy, CT TAP, FNAC, Core Bx | Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with signet cell | Emergency laparotomy, loop colostomy, palliative chemotherapy |
The time from initial diagnosis to metastasis to the breast varies between 1 month and 15 years, average between 1 and 5 years. Hasukic et al. [9] reported a 69 year old patient who had breast metastasis 30 months after the APR. Ting Wang et al. reported a 38 year old male who underwent anterior resection developing breast metastasis after 7 years.
Differentiating primary from metastatic breast neoplasms is not always easy. Mammograms help in settling doubts. The classic mammographic finding is a rounded, well-circumscribed mass no speculation, microcalcification or thickening of the skin [1, 4]. Typical ultrasound (US) features of haematogenous metastases include single or multiple, round to oval shaped, well-circumscribed hypo-echoic masses without spiculations, calcifications, or architectural distortion located superficially in subcutaneous tissue or immediately adjacent to the breast parenchyma.
Histologically, the metastatic tumours show the morphological characteristics of the primary tumours. Excisional or incisional biopsy is the most commonly used procedure for the differential diagnosis [10]. There is increasing use of needle core biopsy rather than fine needle aspiration cytology. Silverman in his study reported 2529 FNA breast biopsies, 666 were malignant, only 18 of these were from extra-mammary malignancies. Alvardo et al. in his series of 10 650 breast biopsies in Mexican population, reported 24 extra-mammary cases.
In majority cases, immune-histochemistry can help to make an accurate diagnosis. Testing for expression of CK7 and CK20 is considered to be most beneficial. The great majority of primary breast cancers are CK7-positive and CK20-negative, while colorectal carcinomas are usually CK7-negative and CK20-positive. Mucinous differentiation of colorectal cancer is associated with poor outcome. In our patient, rectal tumour showed mucinous differentiation with features of signet ring cell subtype which explains the poor response to the neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Most patients succumb to the aggressive course of the disease within a year after the diagnosis of the primary tumour. Surgical treatment of secondary breast cancer is usually palliative. Mastectomy has no significant role, systemic chemotherapy is necessary in these patients. Metastasectomy with effective systemic chemotherapy can prolong survival of these patients [1, 4]. However, its role is mostly palliative.
Treatment options for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) have changed considerably with the introduction of antiepidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) therapies targeting EGFR transduction cascade. KRAS genotyping is mandatory in mCRC treatment prior to undertaking (EGFR) monoclonal antibody therapy. KRAS mutations have been identified as a reliably strong negative predictive factor to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody therapies in mCRC patients.
In conclusion, a new breast mass in a patient with a known primary rectal tumour has to be considered as a breast metastasis until proven otherwise despite its rare occurrence!
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
None declared.



