-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Yousuke Kinjo, Yasushi Adachi, Kunihiko Seki, Michihiko Tsubono, Laparoscopic resection for torsion of an omental lipoma presenting as an acute abdomen in a 5-year-old girl, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2014, Issue 7, July 2014, rju072, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rju072
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Primary tumors of the greater omentum are rare. We report a case of a 5-year-old girl presenting with an acute abdomen who had omental torsion caused by a giant lipoma of the greater omentum, which was diagnosed by a computed tomography scan. Laparoscopy revealed a yellow tumor of the greater omentum with a smooth surface. Tumor excision and partial omentectomy was performed to treat the torsion, and the tumor was retrieved through a 4-cm-wide abdominal incision. Macroscopically, the specimen was 80 × 60 × 25 mm in size and 74.8 g in weight, and histopathological findings were consistent with the diagnosis of lipoma. The present case highlights the possible use of laparoscopic surgery for removing large abdominal lipomas, thus avoiding the drawbacks of laparotomy in terms of postoperative pain and prolonged hospital stay.
INTRODUCTION
Lipomas are benign neoplasms of adipose tissue that may occur anywhere in the body. Although lipomas are the most common mesenchymal tumor, incidence varies depending on the organ or tissue involved. Lipomas of the greater omentum are rare [1] and have only been documented as individual case reports. A handful of cases have been described in children [2–9]. Here, we present a rare case of a symptomatic omental lipoma in a 5-year-old girl which was successfully treated by laparoscopic resection.
CASE REPORT
A 5-year-old Japanese preschool girl presented with a 1-week history of right lower abdominal pain of increasing severity that was associated with nausea and anorexia. She had no history of similar episodes of abdominal pain. On physical examination, her temperature was 38.1°C and her abdomen was tender in the right lower quadrant with signs of peritoneal irritation. No masses were palpable. Laboratory investigation revealed a white blood cell count of 10 000/mm3 with 77% segmented neutrophils. No abnormalities were noted in the plain abdominal radiograph. A contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen revealed linear folds of omental tissue in a concentric pattern that extended from the level of the transverse colon to the right lower abdomen (Fig. 1A). A pelvic mass of 6 cm in diameter with the same uniform radiodensity as that of fatty tissue was also observed (Fig. 1B).
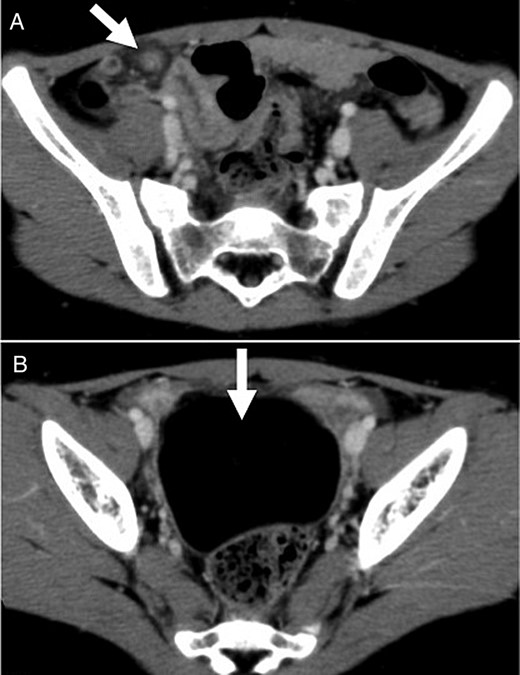
Contrast-enhanced CT scan showed (A) torsion of the omentum, which was seen as linear folds of omental tissue in a concentric pattern that extended from the level of the transverse colon to the right lower abdomen; and (B) a pelvic mass of 6 cm in diameter with the same uniform radiodensity as fatty tissue.
The patient was taken to the operating theater for abdominal laparoscopy because of torsion of the greater omentum. The procedure was performed using a 12-mm trocar placed in the umbilicus with accessory trocars in the left lower quadrant (12 mm) and below the umbilicus (5 mm). Laparoscopy revealed a well-encapsulated, 6 × 5 cm, smooth, yellowish mass originating from the greater omentum that occupied the entire pelvis. A small amount of serous fluid was present in the lower abdomen. The twisted omental pedicle was seen just below the transverse colon, and the lower part of the omentum distal to the torsion point appeared necrotic (Fig. 2). Laparoscopic resection of this necrotic omentum was performed using an ultrasonic coagulation device (Harmonic, Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc., USA). A small abdominal incision ∼4 cm in length was made below the umbilical trocar and the tumor was retrieved through this opening using an Endocatch II (Tyco Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan) without injury to the capsule. The tumor was removed en bloc. The total operation time was 62 min, and only a small amount of blood loss occurred.
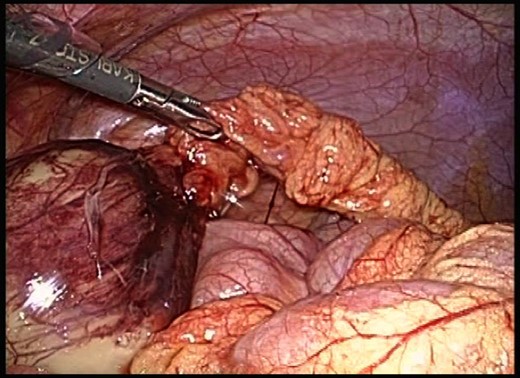
Laparoscopy revealed a tumor at the right lower border of the greater omentum with a smooth surface. Laparoscopic resection of the necrotic omentum was performed using an ultrasonic coagulation device.
Macroscopically, the specimen was 80 × 60 × 25 mm in size and weighed 74.8 g. Histopathological examination revealed that the tumor was composed of mature adipocytes indistinguishable from normal adipose tissue, confirming that it was a lipoma (Fig. 3). Postoperative recovery was uneventful and the patient was discharged on postoperative day 5.
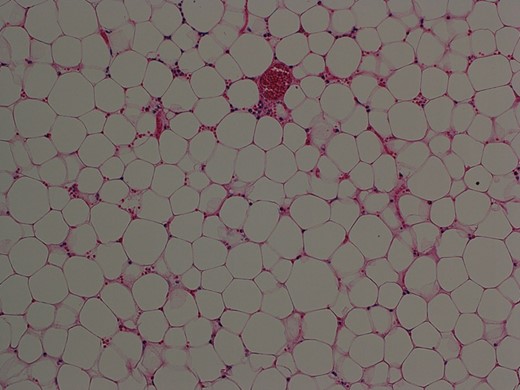
Histopathological examination of the resected specimen showed that the tumor was composed of mature fat cells (hematoxylin and eosin, original object magnification ×10).
DISCUSSION
We described a rare case of omental torsion caused by a giant lipoma in a 5-year-old girl. To our knowledge, this is the first report of a giant lipoma of the greater omentum in a pediatric patient that was treated by laparoscopic surgery.
The incidence of primary tumors of the greater omentum is low, but these tumors are diverse in their pathology. Tumors of the greater omentum originate from its constituents of fat tissue and blood and lymphatic vessels, and present as leiomyoma, leiomyosarcoma, fibroma, fibrosarcoma, hemangiopericytoma, lipoma, liposarcoma, and mesothelioma [1]. Lipomas of the greater omentum are rare, particularly in children, and only a few case reports have been described in the literature. The eight cases of child (patients under 20 years old) omental lipoma reported to date are listed in Table 1, including our present case [2–9]. The most common presenting symptoms were abdominal mass, nausea and fever also occurring occasionally. In our patient, the symptoms and signs of omental torsion seen at first physical examination mimicked those of acute appendicitis. CT scan was useful in determining the relationship between the lipoma and the omental torsion. Similarly, Beattie et al. [10] also reported torsion of the greater omentum associated with a lipoma in a 77-year-old woman who presented with an emergency case of lower abdominal pain.
Cases of lipoma of the greater omentum in a child (patients under 20 years old)
| Case . | Authors (publication year) . | Age . | Sex . | Treatment . | Tumor size (cm) . | Tumor weight (g) . | Symptoms . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Haller et al. (1978) | 3 y | F | Excision (Open) | 8 × 5 × 4 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 2 | Giubilei et al. (1980) | 8 y | M | Excision (Open) | 18 × 15 × 8 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 3 | Joulak et al. (1998) | 3 y | M | Excision (Open) | 13 × 9 × 6 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 4 | Barauskas et al. (2004) | 8 y | F | Excision (Open) | 10 × 11 × 8 | 720 | Abdominal mass |
| 5 | Luo et al. (2005) | 11 m | M | Excision (Open) | 21 × 15 × 12 | 1820 | Abdominal fullness |
| 6 | Srinivasan et al. (2009) | 9 m | NR | Excision (Open) | NR | 1500 | Abdominal mass |
| 7 | Abubakar et al. (2009) | 13 y | F | Excision (Open) | 34 × 26 × 22 | 12 300 | Abdominal mass |
| 8 | Chaudhary et al. (2011) | 2 y | M | Excision (Open) | NR | NR | Abdominal mass and pain |
| 9a | Present case (2013) | 5 y | F | Excision (Laparoscopic) | 8 × 6 × 3 | 75 | Abdominal pain, fever |
| Case . | Authors (publication year) . | Age . | Sex . | Treatment . | Tumor size (cm) . | Tumor weight (g) . | Symptoms . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Haller et al. (1978) | 3 y | F | Excision (Open) | 8 × 5 × 4 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 2 | Giubilei et al. (1980) | 8 y | M | Excision (Open) | 18 × 15 × 8 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 3 | Joulak et al. (1998) | 3 y | M | Excision (Open) | 13 × 9 × 6 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 4 | Barauskas et al. (2004) | 8 y | F | Excision (Open) | 10 × 11 × 8 | 720 | Abdominal mass |
| 5 | Luo et al. (2005) | 11 m | M | Excision (Open) | 21 × 15 × 12 | 1820 | Abdominal fullness |
| 6 | Srinivasan et al. (2009) | 9 m | NR | Excision (Open) | NR | 1500 | Abdominal mass |
| 7 | Abubakar et al. (2009) | 13 y | F | Excision (Open) | 34 × 26 × 22 | 12 300 | Abdominal mass |
| 8 | Chaudhary et al. (2011) | 2 y | M | Excision (Open) | NR | NR | Abdominal mass and pain |
| 9a | Present case (2013) | 5 y | F | Excision (Laparoscopic) | 8 × 6 × 3 | 75 | Abdominal pain, fever |
NR, not reported; y, years; m, months.
aCases complicated by torsion.
Cases of lipoma of the greater omentum in a child (patients under 20 years old)
| Case . | Authors (publication year) . | Age . | Sex . | Treatment . | Tumor size (cm) . | Tumor weight (g) . | Symptoms . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Haller et al. (1978) | 3 y | F | Excision (Open) | 8 × 5 × 4 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 2 | Giubilei et al. (1980) | 8 y | M | Excision (Open) | 18 × 15 × 8 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 3 | Joulak et al. (1998) | 3 y | M | Excision (Open) | 13 × 9 × 6 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 4 | Barauskas et al. (2004) | 8 y | F | Excision (Open) | 10 × 11 × 8 | 720 | Abdominal mass |
| 5 | Luo et al. (2005) | 11 m | M | Excision (Open) | 21 × 15 × 12 | 1820 | Abdominal fullness |
| 6 | Srinivasan et al. (2009) | 9 m | NR | Excision (Open) | NR | 1500 | Abdominal mass |
| 7 | Abubakar et al. (2009) | 13 y | F | Excision (Open) | 34 × 26 × 22 | 12 300 | Abdominal mass |
| 8 | Chaudhary et al. (2011) | 2 y | M | Excision (Open) | NR | NR | Abdominal mass and pain |
| 9a | Present case (2013) | 5 y | F | Excision (Laparoscopic) | 8 × 6 × 3 | 75 | Abdominal pain, fever |
| Case . | Authors (publication year) . | Age . | Sex . | Treatment . | Tumor size (cm) . | Tumor weight (g) . | Symptoms . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Haller et al. (1978) | 3 y | F | Excision (Open) | 8 × 5 × 4 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 2 | Giubilei et al. (1980) | 8 y | M | Excision (Open) | 18 × 15 × 8 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 3 | Joulak et al. (1998) | 3 y | M | Excision (Open) | 13 × 9 × 6 | NR | Abdominal mass |
| 4 | Barauskas et al. (2004) | 8 y | F | Excision (Open) | 10 × 11 × 8 | 720 | Abdominal mass |
| 5 | Luo et al. (2005) | 11 m | M | Excision (Open) | 21 × 15 × 12 | 1820 | Abdominal fullness |
| 6 | Srinivasan et al. (2009) | 9 m | NR | Excision (Open) | NR | 1500 | Abdominal mass |
| 7 | Abubakar et al. (2009) | 13 y | F | Excision (Open) | 34 × 26 × 22 | 12 300 | Abdominal mass |
| 8 | Chaudhary et al. (2011) | 2 y | M | Excision (Open) | NR | NR | Abdominal mass and pain |
| 9a | Present case (2013) | 5 y | F | Excision (Laparoscopic) | 8 × 6 × 3 | 75 | Abdominal pain, fever |
NR, not reported; y, years; m, months.
aCases complicated by torsion.
Lipomas of the omentum are easily discovered by ultrasound examination and appear as a well-encapsulated, echogenic mass with good sound transmission [2]. CT scan provides definitive identification of fat content within the lesion by providing radiodensity measurements.
Surgery is the mainstay treatment of omental lipomas. Intraperitoneal lipomas, particularly lipomas of the greater omentum, are easily removed. The rate of recurrence after excision is <5%. We decided to perform laparoscopic tumor excision and partial omentectomy because of torsion of the omentum. Since the advent of laparoscopy, it has become the preferred procedure for many thoracic and abdominal conditions. Patients treated using this approach have decreased need for narcotic analgesics, shorter hospitalization, quicker recovery and excellent cosmetic results. Thanks to these advantages, the applications of laparoscopic surgery continue to expand. Laparoscopy plays an important role in the diagnosis of tumors, particularly abdominal tumors in children, the diagnosis and management of which may be challenging. Correct diagnosis and treatment depend on adequate tissue procurement for histological analysis. CT-guided needle biopsies may not yield sufficient tissue for all studies, whereas adequate tissue can be procured and tumor resectability assessed using laparoscopy. Laparoscopy for pediatric abdominal tumors has been mostly used for neuroblastomas, most cases of which were identified by mass screening and were consequently small.
In summary, we presented a pediatric case of torsion of the greater omentum caused by an omental lipoma that was treated by laparoscopic resection. Laparoscopic surgery avoids the complications and postoperative pain associated with laparotomy.



