-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Abdullah M Alqahtani, Fahad A Alwadi, Mohammed Almahdi, Actinomycosis of the paranasal sinuses: case report and literature review, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2023, Issue 8, August 2023, rjad436, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjad436
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Actinomycosis is a chronic granulomatous condition caused by filamentous gram-positive anaerobic bacteria that colonizes the mouth, gastrointestinal tract and urogenital tract. Infection occurs through the mucosal surfaces, often resulting from dental procedures or trauma, primarily affecting the maxillary sinus. We report a case of Actinomyces sinusitis affecting the right maxillary and right ethmoidal sinuses of a 41-year-old woman. The diagnosis was made through a combination of histopathological report and computed tomography scan. The patient underwent endoscopic sinus surgery followed by long-term antibiotics for 6 months and reported improvement of her symptoms.
INTRODUCTION
Actinomycosis is a rare, long-lasting inflammatory disease that occurs due to bacterial species of Actinomycetaceae. These bacteria are filamentous gram-positive anaerobic species that normally colonize the mouth, gastrointestinal tract and urogenital tract [1, 2]. Actinomycosis can only penetrate the mucosal surfaces and cause infection through facial injuries or trauma [3]. Typically, this occurs after dental procedures, and it seldom impacts the nasal cavity and adjacent sinuses. The maxillary sinus is the most frequent sinus to be affected, but it’s also possible for the ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses to be involved [4]. This paper describes a case of Actinomycosis of the paranasal sinuses.
CASE REPORT
A 41-year-old woman presented to the ENT clinic in January 2020 with right clear to yellowish rhinorrhea. The nasal discharge started 2 months after her cesarean section delivery. On physical examination, nose vestibulitis was noted for that she was treated with antibiotics (Augmentin) for 1 week that significantly improved her symptoms. However, the patient presented 5 months later with 2 weeks history of brownish-to-greenish nasal discharge, in which she was treated again with Augmentin, along with nasal hypertonic saline and mometasone furate sprays. Rhinosinusitis and CSF rhinorrhea were suspected, and a computed tomography (CT) was done. Upon reviewing the CT, it showed complete opacification of the right maxillary and right ethmoidal sinuses with calcifications in the ethmoidal sinus with right ostiomeatal complex obstruction, and mild mucosal thickening at the right frontal sinus with no significant bone lesion (Fig. 1A). The left side sinuses were unremarkable while there was mild nasal septal deviation to the right. She was booked for functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) + septo-turbinoplasty (STP), however, it was postponed due to COVID lock down. The patient was referred to the dental department for root canal therapy.
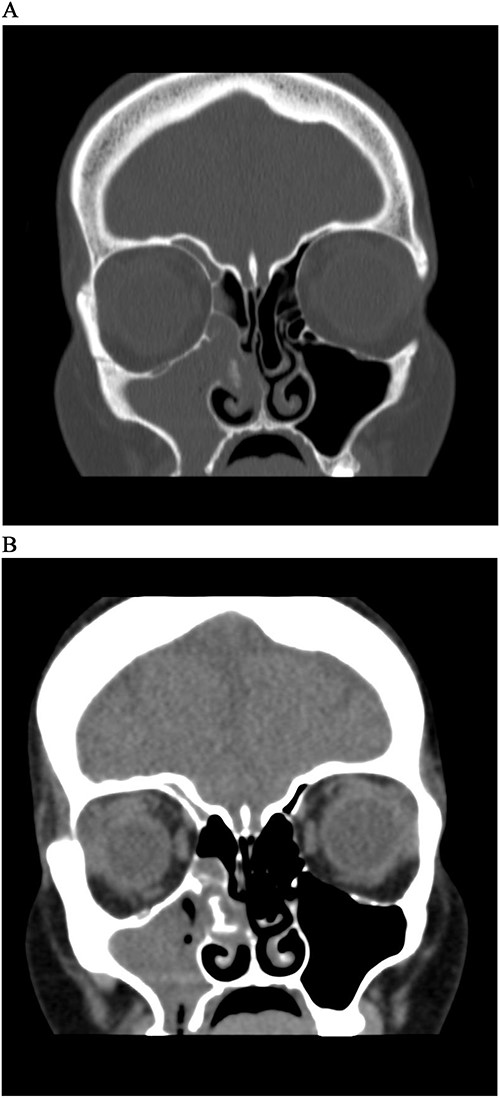
CT Sinus, bone window (A) and soft tissue window (B), coronal cut, shows complete opacification of right maxillary sinus and anterior ethmoidal cells, with a soft tissue mass extending from MM to septum with hyperdensity lesion.
The patient underwent FESS + STP. Intra-operative examination showed mucopurulent discharge coming from the right nostril, so a swab was taken and sent for culture and sensitivity. Following that, 0° rigid scope revealed the presence of granulation tissue filling the right nostril and a query foreign body that were removed and sent for histopathology (Fig. 2). Septoplasty was done and there was also granulation tissue originating from right posterior septum which caused septal perforation. Moreover, examination of middle meatus (MM) and maxillary antrum also showed granulation tissue with mucopurulent discharge, in which maxillary sinus was opened and cleaned along with anterior and posterior ethmoid sinuses (Fig. 3). The pathology report revealed the presence of acute inflammation and bacterial colonies morphologically suggestive of actinomyces species. She was started on Augmentin 1 gram BID, with nasal irrigation and she was referred to infectious diseases service and they continued Augmentin treatment 6 months. Patient reported improvement of her symptoms.
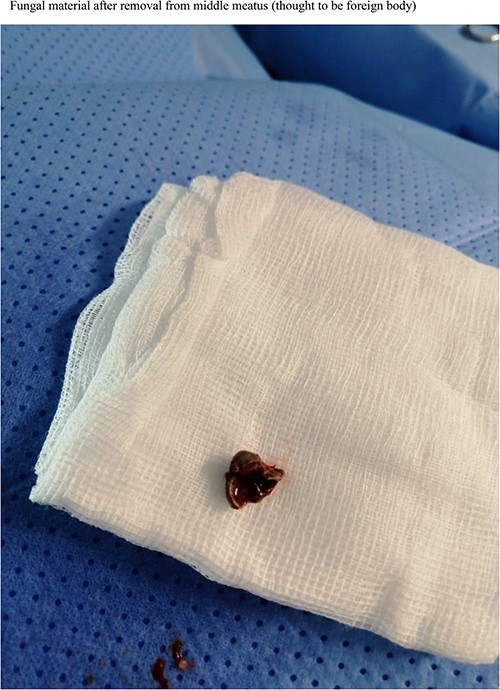
Fungal material after removal from middle meatus (thought to be foreign body).
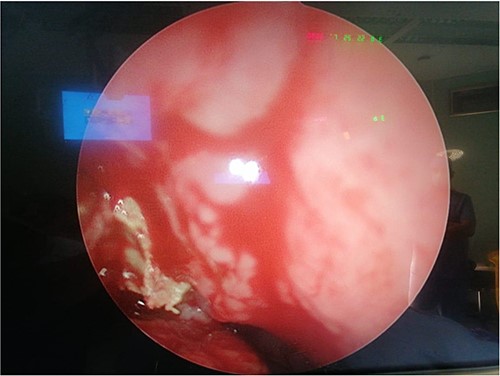
Intra-operative photo shows fungal material with pus discharge in middle meatus.
DISCUSSION
Actinomycosis is an uncommon chronic bacterial disease that infects patients with risk factors such as dental operations, diabetes, immunosuppression, poor dental hygiene [1]. Actinomyces infection presents differently based on the site where the infection occurs. Common forms include orocervicofacial abscesses for patients with bad oral hygiene and dental issues, chest infections due to aspiration of gastric content, infections in the abdomen after surgery or gastrointestinal damage and infections in the pelvic area for those with intrauterine contraceptive devices [5–7]. Cervicofacial actinomycosis, which accounts for ⁓50% of all recorded cases, is the most common type of actinomycosis, followed by abdominal and thoracic actinomycosis (15–20%) [2, 8]. Although it’s very rare for actinomyces to infect the sinuses, a few cases were reported [9–13]. Jason E. Cohn et al. reported a case of unilateral maxillary sinus actinomycosis with a closed oroantral fistula 2 weeks after the patient had upper molar extraction. The patient presented with right facial pain, tenderness, as well as right ear fullness, pressure and hearing loss. A CT scan of the sinuses showed that the right maxillary sinus was completely opacified [9]. However, in our case the patient only presented with recurrent rhinorrhea and had complete opacification of both the right maxillary and ethmoidal sinuses (Fig. 1). Another study done in Korea analyzed the medical records of six patients with actinomycosis of the paranasal sinus in which all lesions affected the maxillary sinus unilaterally [10]. Similar to our case, a patient in Brazil suffering from chronic sinusitis was unresponsive to medical therapy due to the presence of actinomyces [11]. The present case report demonstrates analogous CT scan characteristics between fungal and Actinomyces infections which is consistent with the existing literature [12, 14]. While only the maxillary and ethmoidal sinuses were affected in our case, invasive actinomyces in another patient resulted significant damage to the maxilla, nasal bones and all three sinuses (maxillary, frontal and ethmoidal) [13].
The diagnosis of actinomycotic sinusitis can be challenging without the histopathological results as it shares similar findings with fungal sinusitis on CT scans (e.g. the shadow in unilateral sinus with a calcified density, hypertrophic maxillary bone) [14]. The gram stain is the preferred method over culture for detecting an actinomyces infection due to its high sensitivity. However, it is crucial to diagnose actinomycosis and select appropriate antibiotics using culture and pathology techniques to isolate the bacteria because of the polymicrobial nature of the disease [15]. Our patient underwent surgery, and a biopsy was taken to the pathology that showed numerous bacterial colonies morphologically suggestive of actinomyces species. The gold standard treatment for actinomycotic sinusitis is generally considered to be long-term antibiotics (such as penicillin) therapy after endoscopic sinus surgery [9–13]. Just like our patient, three cases reported treating their patients with endoscopic sinus surgery and were given long-term antibiotics (e.g. Augmentin) for a duration of 4–6 months (9–11). One case due to the presence of aspergillosis, treated their patient with Augmentin intravenously for 5 days and orally for 3 weeks, along with saline irrigation following the surgery [12].
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, actinomycosis of the paranasal sinuses is extremely rare, and often mistaken with fungal infection due to the similarities seen on CT scan. This patient was diagnosed as a case of actinomycotic sinusitis using a combination of histopathological report and CT scan. The patient was treated with endoscopic sinus surgery followed by long-term antibiotics and is recovering well.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
FUNDING
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
DATA AVAILABILITY
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding aurthor upon request.



