-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Lama Kadoura, Amr Hamza, Afnan W M Jobran, Yousef Mahmoud Nimer Habes, Sarab Agha, Rama Alyousfi, Kusay Ayoub, Unicentric Castleman disease in the mesentery with ambiguous symptoms: a rare case report, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2021, Issue 8, August 2021, rjab367, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjab367
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Castleman disease (CD) is a rare clinical entity characterized by enlarged lymph nodes. It may affect a single lymph node (unicentric) or multiple lymph nodes in the body (multicentric). However, it is exceptionally uncommon for unicentric Castleman disease (UCD) to present in the mesentery. Herein, we report a case of 38-year-old female complaining of polymenorrhea and abdominal discomfort for 4 months. Her past medical history was unremarkable; however, she has started smoking recently. The physical examination and radiography indicated a large, well-defined mass in the right hypochondrium. Eventually, the patient underwent laparotomy and the mass was excised totally. The Pathologic study confirmed the diagnosis as mesenteric CD, hyaline-vascular type. After 5 months of follow-up, the patient showed no evidence of recurrence. In conclusion, this case underscores the importance of taking mesenteric CD into consideration in each patient who presents with solid abdominal mass or ambiguous abdominal discomfort.
INTRODUCTION
Castleman disease (CD) is a rare lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by lymph nodes enlargement. CD affects a single lymph node (unicentric) or multiple lymph nodes in the body (multicentric) [1]. The latter could be associated with HHV-8 infections in HIV-infected individuals, however, the etiology of CD is still uncertain [1, 2].
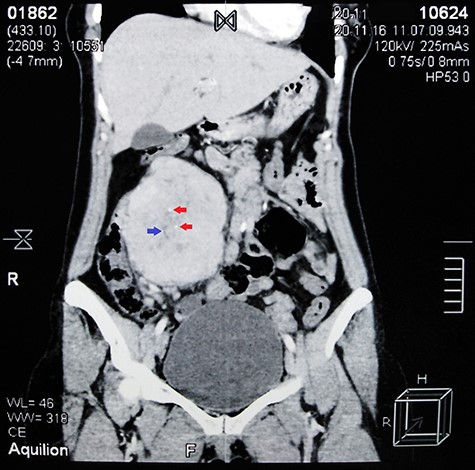
Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan shows a large heterogeneous mass adjacent to the inferior margin of the liver measuring (11.5 × 8.5 × 9 cm) and containing calcified areas (red arrows) and necrosis (blue arrow).
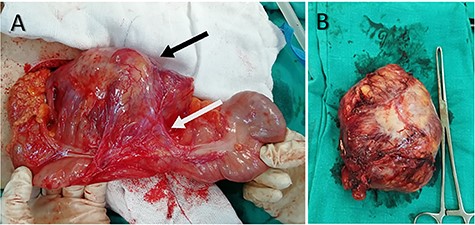
(A) Intraoperative image shows the large well-defined mass that locates in the mesentery (black arrow) and is attached to the ascending colon (white arrow). (B) The mass after resection.
Unicentric Castleman Disease (UCD) mainly occurs in the mediastinum (70% of cases), whereas mesenteric disease is extremely rare and usually found in multicentric type. UCD is usually asymptomatic but it may be manifested with symptoms resulting from compression of adjacent organs [1]. The treatment of choice in UCD is typically a complete ‘en bloc’ surgical resection [3].
Herein, we report a case of mesenteric CD diagnosed incidentally in a 38-year-old female after gynecological clinic visit. The patient was successfully diagnosed and recovered after appropriate evaluation and surgery.
CASE REPORT
A 38-year-old Caucasian female with no significant prior medical history presented to the gynecological clinic with polymenorrhea. Upon taking a detailed medical history, the patient mentioned a 4-month history of abdominal discomfort in the right hypochondrium that increased gradually. She described it as a fullness feeling which was exacerbating after eating. The patient’s obstetric history was unremarkable, except for a cesarean section 6 years ago. She is a current smoker and has a positive family history of hypertension and DM type 2.
On physical examination, the abdomen appeared soft, not distended and non-tender with a palpable mass in the right hypochondrium. In addition, her vital signs were within normal. Laboratory findings showed decreased RBC count (3.2 × 106/μl), hemoglobin (10.9 g/dl) and hematocrit (32.2%) which indicated anemia.
Abdominal ultrasound (US) revealed normal findings except for a 9.1 × 7.3 cm heterogeneous mass in the right hypochondrium, and an ~5 cm cystic lesion on the left ovary. Contrast abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan showed a (11.5 × 8.5 × 9 cm) well-defined mass adjacent to the inferior margin of the liver with calcified areas (Fig. 1). Para-aortic lymph nodes were not enlarged.
As the diagnosis was unclear, laparotomy was performed. Intraoperative inspection showed a large mass occupying the mesentery (Fig. 2). The mass was totally excised after releasing the adhesions with the ascending colon. Pathology specimens revealed prominent, hyalinized penetrating capillaries, rearranged lymphocytes and regression in lymph follicles; these findings were consistent with CD hyaline-vascular type (Fig. 3).
The post-operation period was uneventful and 5-month follow-up, which consisted of a single CT scan and regular clinical examinations, showed no evidence of recurrence (Fig. 4).
DISCUSSION
CD is considered a rare benign lymphoproliferative disease with an estimated incidence rate of 21/million [4]. CD was first described by Benjamin Castleman in 1954, and the disease is also known as angiomatous lymphoid hyperplasia or giant lymph node hyperplasia [5]. Although some reports indicated the close relationship between CD and the proliferation of T cells and B cells stimulated by interleukin 6, the pathogenesis of CD is still unclear making the diagnosis difficult [6].
UCD can occur in all lymph nodes in the body but it usually involves the mediastinum. Extrathoracic disease has been reported in the neck, axilla, pelvis and retroperitoneum; however, its occurrence in the mesentery is more rare, and only 53 similar cases were registered in the literature until 2017 according to Bacale et al. [1, 7]. In our case, the mass was in the mesentery, which represents a rare region to occur. UCD is generally asymptomatic but may present as compressive symptoms. However, Bejjani et al. [3] indicated that an extreme minority of CD patients had anemia at presentation [1]. However, these findings were consistent with our patient.
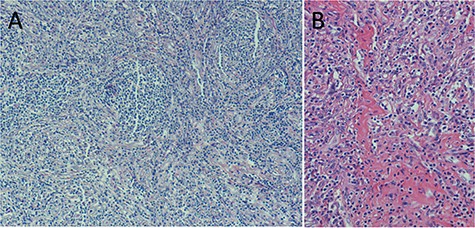
(A) Microscopic examination based on Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stain reveals atrophy of follicles and onion skin appearance. (B) Prominent vascular proliferation and hyalinization of vessel walls.
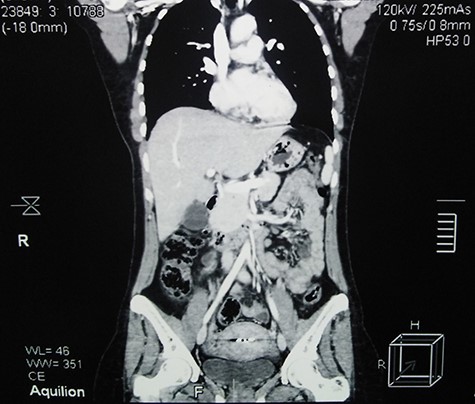
Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan 5 months after surgery shows full recovery and no evidence of recurrence.
Due to the resemblance of UCD images with varied masses, it is important to differentiate between UCD and other disorders that can present as a solitary enlarged lymph node and/or systemic symptoms such as Toxoplasma lymphadenitis, HIV lymphadenitis, follicular hyperplasia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes [8].
In UCD, a single, well-defined, enlarged lymph node associated with moderate to intense post-contrast enhancement is often characteristic features of UCD on CT. In addition, calcifications are seen in only 5–10% of CD patients [9].
According to the pathological results, CD is divided into three types: hyaline vascular type, plasma cell type and mixed type. The hyaline-vascular type represents ~80–90% of CD and tends to appear more frequently in UCD. It is characterized by prominent vascular proliferation, hyalinization of vessel walls and atretic germinal centers traversed by penetrating vessels resulting in ‘lollipop’ follicles. The lymphocytes in the surrounding mantle zones are also consequently rearranged imparting ‘onion-skinned’ follicles. In addition, the interfollicular areas typically show an extensive vascular proliferation with perivascular hyalinization [1, 7].
In UCD, surgery is usually curative in which the lesions are removed completely or partially [3]. Furthermore, systemic steroids may provide symptomatic relief, and radiation therapy could be considered. Prognosis in UCD is excellent and patients are usually cured after lymph node excision. Patients may develop lymphoma and/or paraneoplastic pemphigus which could lead to fatal consequences for UCD patients [8]. Regarding this case, removing the mass completely showed acceptable results and 5-month follow-up after surgery showed no evidence of recurrence.
In conclusion, CD is an unusual medical case that is frequently ignored due to clinical polymorphism and diagnostic challenges. Despite its rarity, UCD should be investigated when solid abdominal mass or ambiguous abdominal discomfort is found. Oftentimes, surgical excision is considered both diagnostic and therapeutic approach with acceptable results during long-term follow-up.
AUTHOR’S CONTRIBUTIONS
K.A. performed the surgery in Aleppo University Hospital. S.A. performed the histological examination and revised the final draft. L.K. performed data collection and revision. A.H., A.J., Y.H. and R.A. analyzed and interpreted the patient data, and wrote the manuscript. A.H. is the corresponding author. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to thank Dr. Owais Aleter from the Department of Radiology for contribution in this work.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors report no conflicts of interests.
FUNDING
No funding was received for the work involved in this article.
ETHICAL APPROVAL
Not required for case reports at our hospital. Single case reports are exempt from ethical approval in our institution.
INFORMED CONSENT
Patient’s consent was obtained for the publication of this case report. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal upon request.



