-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Omar Iziki, Sami Rouadi, Redallah Larbi Abada, Mohamed Roubal, Mohamed Mahtar, Bilateral antrochoanal polyp: report of a new case and systematic review of the literature, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2019, Issue 3, March 2019, rjz074, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjz074
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Antrochonal polyp (ACP) is a benign, rare, and generally unilateral tumor which originates from the maxillary sinus mucosa. Bilateral ACP is extremely rare. Only few cases have been documented in the literature until 2018. The authors report the case of a 44-year-old women, who presented with a bilateral progressive nasal obstruction for the past 2 years, slight headache and a decreased sense of smell has been started in last four months. Nasal endoscopy revealed pale polypoidal masses in nasal cavities, arising from each middle meatus and extending to the nasopharynx. Computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses revealed the presence of soft-tissue masses in the maxillary sinuses, passing through the maxillary ostium, and extending into the corresponding nasal cavities, and posteriorly upto the nasopharynx. The other sinuses were normally aerated. The tumors were removed surgically with a nasal endoscopy technique. Histopathology examination the two lesions revealed benign inflammatory nasal polyps.
INTRODUCTION
Antrochonal polyp is a benign tumor that originates from the maxillary sinus mucosa, prolapses into the nasal cavity through the maxillary ostium, and may reaching the choana and nasopharynx. It was described for the first time by Professor Gustav Killian, in 1906 [1].
Antrochoanal polyps are generally unilateral in occurrence and seen mostly in children and adolescents, bilateral antrochonal polyp are extremly rare [2]. Only 11 cases have been reported in the English scientific literature until April 2017. In this article, we presented a new rare case of bilateral antrochoanal polyp.
CASE REPORT
We report the case of a 44-year-old female patient, without important pathological antecedents (no history of associated asthma or allergy), who was referred to our ENT clinic with a 2-year history of bilateral progressive nasal obstruction, slight headache and a decreased sense of smell has been started in last four months.She denied other nasal symptoms such as rhinorrhea, epistaxis, sternutation crises, itching, and no otologique or pharyngolaryngeal symptoms.
Anterior rhinoscopy and nasofibroscopique revealed pale polypoidal masses in both nasal cavities, arising from each middle meatus and extending to the nasopharynx (Fig. 1).
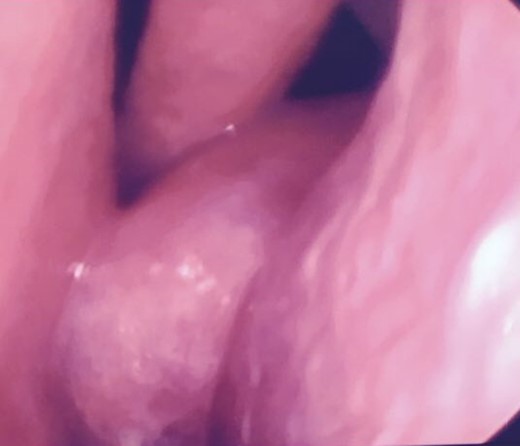
Computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses disclosed an almost complete opacification of the maxillary sinuses and the presence of a soft-tissue masses passing through the maxillary ostium and extending into the corresponding nasal cavities and posteriorly upto the nasopharynx. The other sinuses were normally aerated (Fig. 2).
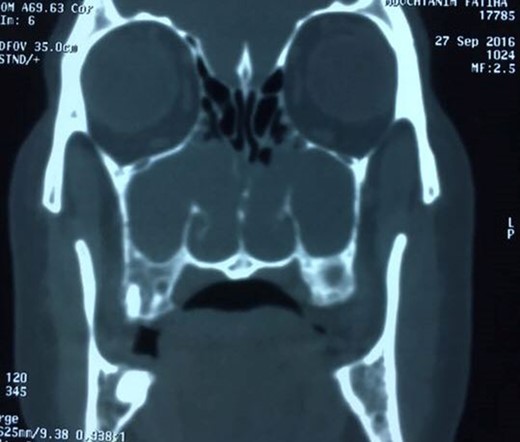
Surgery was performed exclusively by nasal endoscopy, and the polyps were removed under general anesthetic using functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) with bilateral uncinectomy, middle meatal antrostomy and bilateral polypectomy.
Histopathologic examination the two lesions revealed benign inflammatory nasal polyps. The patient experienced a complete recovery with resolution of complaints and no recurrence one year postoperatively.
DISCUSSION
Antrochoanal polyps are infrequent benign nasal masses, it’s a unilateral condition mainly affecting young people, representing between four to six per cent of all nasal polyps [3].
The pathogenesis and etiology of ACPs are still unknown [4]. In 1988, Berg et al. hypothesized that ACP could arise from an antral cyst [5]. Recently, Frosini et al., in the largest study of 200 cases, suggested that, in a patient with a pre-existing silent antral cyst, an association of inflammatory-anatomical alteration at ostio-meatal complex/middle meatus level, can forced the polyp to herniate outside, through the accessory ostium [1].
It is important to note that ACP can be associated with same chronic inflammatory condition (allergic or infectious), but the factors of cause and effect remain controversial [3].
Macroscopically, the antrochoanal polyp is composed usually of three part: a cystic or antral part filling the maxillary sinus and a solid part arising from the natural or accessory maxillary ostium into the middle meatus (nasal part), and choanal part [1].
Cases of bilateral ACP are extremely rare. In 1995, Myatt and al. descibed the first bilateral ACP in a fit 12-year-old child [2]. In order to obtain more relevant information on this seemingly rare entity, we performed a literature review without language restriction. Our search was conducted in PubMed (up to January, 2018) using the following terms: (Antrochoanal polyp OR bilateral antrochoanal polyp). only eleven articles have been documented in the literature until 2018, that reported 11 cases. Available clinical data were extracted from these articles and summarized in Table 1. Our case was added for analysis purposes.
| Authors . | Age(years)/sex . | Clinical presentation . | Surgical approach . | Histology . | Recurence . | Time of follow-up . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myatt and Cabrera [2] | 12/F | nasal obstruction + rhinorrhoea | FESS | Benign | No | 3 months |
| Basu [4] | 12/F | nasal obstruction | Caldwell-Luc operation | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Jmeian [5] | 6/F | Nasal obstruction | Benign | No | ||
| Konstantinidis [6] | 49/F | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Yilmaz et al. [7] | 24/F | Nasal Obstruction rhinorrhea | FESS | Benign | No | 12 months |
| Sousa et al. [3] | 37/M | Nasal obstruction | Caldwell-Luc Approach and FESS | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Singhal and Gupta [8] | 32/F | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | |
| Sabino et al. [9] | 48/M | Nasal obstruction rhinorrhea, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | 4 months |
| Chodankar and Tiwari [1] | 57/M | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | --- |
| Oner et al. | 20/M | headache rhinorrhea, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | --- |
| Izikiet al. | 44/F | Nasal obstruction headache, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | 12 months |
| Authors . | Age(years)/sex . | Clinical presentation . | Surgical approach . | Histology . | Recurence . | Time of follow-up . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myatt and Cabrera [2] | 12/F | nasal obstruction + rhinorrhoea | FESS | Benign | No | 3 months |
| Basu [4] | 12/F | nasal obstruction | Caldwell-Luc operation | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Jmeian [5] | 6/F | Nasal obstruction | Benign | No | ||
| Konstantinidis [6] | 49/F | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Yilmaz et al. [7] | 24/F | Nasal Obstruction rhinorrhea | FESS | Benign | No | 12 months |
| Sousa et al. [3] | 37/M | Nasal obstruction | Caldwell-Luc Approach and FESS | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Singhal and Gupta [8] | 32/F | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | |
| Sabino et al. [9] | 48/M | Nasal obstruction rhinorrhea, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | 4 months |
| Chodankar and Tiwari [1] | 57/M | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | --- |
| Oner et al. | 20/M | headache rhinorrhea, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | --- |
| Izikiet al. | 44/F | Nasal obstruction headache, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | 12 months |
| Authors . | Age(years)/sex . | Clinical presentation . | Surgical approach . | Histology . | Recurence . | Time of follow-up . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myatt and Cabrera [2] | 12/F | nasal obstruction + rhinorrhoea | FESS | Benign | No | 3 months |
| Basu [4] | 12/F | nasal obstruction | Caldwell-Luc operation | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Jmeian [5] | 6/F | Nasal obstruction | Benign | No | ||
| Konstantinidis [6] | 49/F | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Yilmaz et al. [7] | 24/F | Nasal Obstruction rhinorrhea | FESS | Benign | No | 12 months |
| Sousa et al. [3] | 37/M | Nasal obstruction | Caldwell-Luc Approach and FESS | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Singhal and Gupta [8] | 32/F | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | |
| Sabino et al. [9] | 48/M | Nasal obstruction rhinorrhea, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | 4 months |
| Chodankar and Tiwari [1] | 57/M | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | --- |
| Oner et al. | 20/M | headache rhinorrhea, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | --- |
| Izikiet al. | 44/F | Nasal obstruction headache, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | 12 months |
| Authors . | Age(years)/sex . | Clinical presentation . | Surgical approach . | Histology . | Recurence . | Time of follow-up . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myatt and Cabrera [2] | 12/F | nasal obstruction + rhinorrhoea | FESS | Benign | No | 3 months |
| Basu [4] | 12/F | nasal obstruction | Caldwell-Luc operation | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Jmeian [5] | 6/F | Nasal obstruction | Benign | No | ||
| Konstantinidis [6] | 49/F | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Yilmaz et al. [7] | 24/F | Nasal Obstruction rhinorrhea | FESS | Benign | No | 12 months |
| Sousa et al. [3] | 37/M | Nasal obstruction | Caldwell-Luc Approach and FESS | Benign | No | 6 months |
| Singhal and Gupta [8] | 32/F | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | |
| Sabino et al. [9] | 48/M | Nasal obstruction rhinorrhea, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | 4 months |
| Chodankar and Tiwari [1] | 57/M | Nasal obstruction | FESS | Benign | No | --- |
| Oner et al. | 20/M | headache rhinorrhea, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | --- |
| Izikiet al. | 44/F | Nasal obstruction headache, hyposmia | FESS | Benign | No | 12 months |
We identified ten cases of bilateral ACP, eight females, three males, and patients’ mean age was of 28, ringing from 6 to 57 years. The most common symptom was nasal obstruction. Other symptoms were purulent rhinorrhea, pain, epistaxis or bloody nasal discharge, and sore throat. In all cases the diagnostic is made by nasal endoscopy (polypoid tumor emerging from each maxillary sinus through widened ostia and extending to the nasopharynx), and computed tomography (CT). One surgical procedure was sufficient to eradicate polyps in all cases. Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery was used to remove polyps in nine cases, Caldwell-Luc operation in one case, and together in one case. No major complications occurred, and no recurrence reported. All polyps were described as inflammatory or benign polyps at histological examination. (Table 1)
Bilateral ACP can be especially confused with chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps. A biopsy is mandatory for histopathological confirmation [1].
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, bilateral ACP is a rare entity; endoscopic examination and computed tomography scan are the gold standard tests for diagnosing and adequate preoperative evaluation. The surgical treatment is mandatory, and endoscopic surgery is actually the approach of choice.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
None.



