-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Fatema Alzahraa Almohamad, Tareq Ahmad, Basel Ahmad, Khalid Hussain, Lama Hadid, Majdi Zein, Mohamad Ahmad, False-positive radioiodine accumulation in a huge pelvic mass after thyroidectomy for papillary carcinoma, a case report from Syria, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2018, Issue 2, February 2018, rjy028, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjy028
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Iodine has always been connected to thyroid gland, and the fact that thyroid tissue traps, organificates and stores iodine more than other tissues is well known, hence the use of radioiodine as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool for thyroid disorders. However, false-positive cases do occur. We present a case of a 34-year-old patient who underwent total thyroidectomy for papillary carcinoma. Results of follow up TSH, thyroglobulin and thyroglobulin antibody tests after surgery lead to two rounds of radioactive iodine. After that, a radioiodine whole-body scan showed high uptake in the pelvis above bladder. Computed tomography scan showed a pelvic heterogeneous mass with some calcifications. Surgical removal and subsequent pathology confirmed the absence of metastasis. The final pathological diagnosis was serous cystadenoma, endometriosis cyst and leiomyoma. As the real cause behind false-positive iodine uptake by these tissues has yet to be determined, careful assessment should be considered in any suspicious case.
INTRODUCTION
Radioactive iodine isotopes have proved invaluable in the diagnosis and treatment of thyroid disorders due to the fact that functioning thyroid tissues trap, organificate and store iodine more than other tissues [1].
However, there are many documented cases of unexpected uptake. Theories for this phenomenon of false-positive uptake include: radioiodine thyroid hormone metabolism in other tissues, retention of radioiodinated body fluids, uptake by inflamed tissues, functional sodium iodine symporters or idiopathic [2].
Unfortunately, these false-positive cases are hard to be diagnosed and thus surgery is usually the only means to reach a definitive diagnosis.
Herein we present a case about large volume false-positive radioiodine uptake in the pelvis of a 34-year-old patient in Damascus, Syria.
CASE REPORT
A 34-year-old woman suffered from a neck mass one year before admission to our hospital. Past medical and familial history was not relevant except for her mother having received a total thyroidectomy for benign pathology.
Her family doctor ordered a neck ultrasound, which revealed a suspected thyroid nodule in the right lobe.
TSH level was normal and following frozen section biopsy, which showed papillary carcinoma, the patient went on to receive a total thyroidectomy. Final diagnosis was papillary carcinoma of the thyroid (well-differentiated grade I–II) associated with extracapsular spread and lymphatic invasion.
Seven weeks after surgery, during which time the patient had not taken any levothyroxine, TSH level was 52 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml), thyroglobulin was more than 500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml), thyroglobulin AB was 16.1 uIU/ml (0–40 uIU/ml). The first 100 mCi dose of radioactive iodine was given.
Three months after the first dose, re-evaluation was done, TSH level was 0.1 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml), Thyroglobulin was more than 500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml), Thyroglobulin AB was 18.1 uIU/ml (0–40 uIU/ml).
A second radioactive iodine dose was scheduled (6 months after the first one).
Evaluation before the second dose showed TSH level was 16.4 uIU/ ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml), Thyroglobulin was 1881 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml, and neck ultrasound was negative.
The second I-131 radioactive iodine dose was taken.
Five days later, a whole-body scan (WBS) was performed showing no uptake in the neck but high uptake in the pelvis above the bladder (Fig. 1).
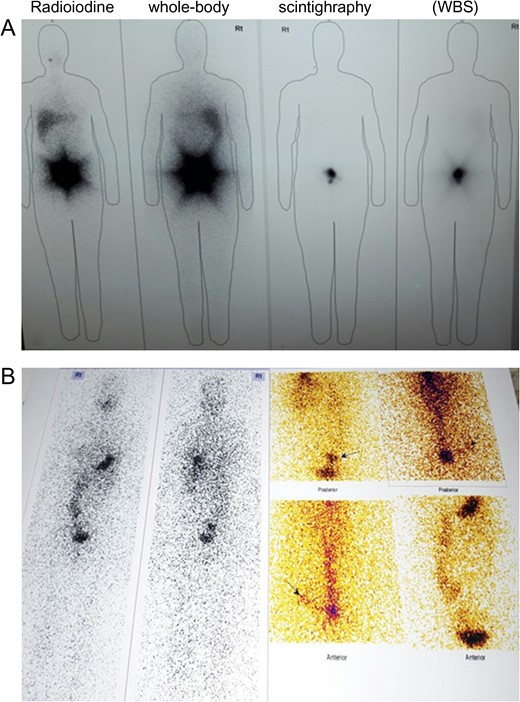
For further investigation, the patient came to our hospital in October 2016; physical examination was normal, lab test results on admission are illustrated in Table 1.
| Test . | Result . | Reference range . |
|---|---|---|
| White blood cells | 6800/ μl | 4400–11 000/ μl |
| Neutrophils percent | 78% | 40–70% |
| Hemoglobin | 10.9 g/dl | 13–16 g/dl |
| Hematocrit | 32.7% | 38–53% |
| Platelets | 205 × 103/ μl | 150–450 × 103/ μl |
| Urea | 18 mg/dl | 10–50 mg/dl |
| Creatinin | 0.5 mg/dl | 0.7–1.36 mg/dl |
| ALT | 11 IU/l | 8–20 IU/l |
| AST | 17 IU/l | 8–20 IU/l |
| PT | 83% | |
| CEA | 0.8 | |
| CA19_9 | 22.7 | |
| CA125 | 18.3 | |
| TSH | 3.4 uIU/ml | 0.4–4 uIU/ml |
| Ft4 | 1.6 |
| Test . | Result . | Reference range . |
|---|---|---|
| White blood cells | 6800/ μl | 4400–11 000/ μl |
| Neutrophils percent | 78% | 40–70% |
| Hemoglobin | 10.9 g/dl | 13–16 g/dl |
| Hematocrit | 32.7% | 38–53% |
| Platelets | 205 × 103/ μl | 150–450 × 103/ μl |
| Urea | 18 mg/dl | 10–50 mg/dl |
| Creatinin | 0.5 mg/dl | 0.7–1.36 mg/dl |
| ALT | 11 IU/l | 8–20 IU/l |
| AST | 17 IU/l | 8–20 IU/l |
| PT | 83% | |
| CEA | 0.8 | |
| CA19_9 | 22.7 | |
| CA125 | 18.3 | |
| TSH | 3.4 uIU/ml | 0.4–4 uIU/ml |
| Ft4 | 1.6 |
| Test . | Result . | Reference range . |
|---|---|---|
| White blood cells | 6800/ μl | 4400–11 000/ μl |
| Neutrophils percent | 78% | 40–70% |
| Hemoglobin | 10.9 g/dl | 13–16 g/dl |
| Hematocrit | 32.7% | 38–53% |
| Platelets | 205 × 103/ μl | 150–450 × 103/ μl |
| Urea | 18 mg/dl | 10–50 mg/dl |
| Creatinin | 0.5 mg/dl | 0.7–1.36 mg/dl |
| ALT | 11 IU/l | 8–20 IU/l |
| AST | 17 IU/l | 8–20 IU/l |
| PT | 83% | |
| CEA | 0.8 | |
| CA19_9 | 22.7 | |
| CA125 | 18.3 | |
| TSH | 3.4 uIU/ml | 0.4–4 uIU/ml |
| Ft4 | 1.6 |
| Test . | Result . | Reference range . |
|---|---|---|
| White blood cells | 6800/ μl | 4400–11 000/ μl |
| Neutrophils percent | 78% | 40–70% |
| Hemoglobin | 10.9 g/dl | 13–16 g/dl |
| Hematocrit | 32.7% | 38–53% |
| Platelets | 205 × 103/ μl | 150–450 × 103/ μl |
| Urea | 18 mg/dl | 10–50 mg/dl |
| Creatinin | 0.5 mg/dl | 0.7–1.36 mg/dl |
| ALT | 11 IU/l | 8–20 IU/l |
| AST | 17 IU/l | 8–20 IU/l |
| PT | 83% | |
| CEA | 0.8 | |
| CA19_9 | 22.7 | |
| CA125 | 18.3 | |
| TSH | 3.4 uIU/ml | 0.4–4 uIU/ml |
| Ft4 | 1.6 |
Ultrasound and computed tomography (CT) were normal except for a pelvic heterogeneous mass with some calcifications adjacent to and causing an impression on the bladder. The mass measured 13 × 8.5 cm (Fig. 2).
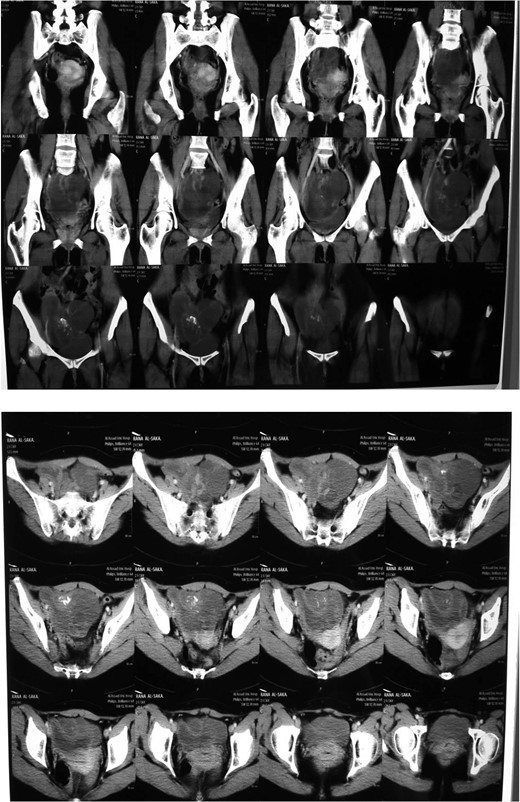
Surgery was scheduled, abdominal exploration was performed and a big mass was detected on the right ovary, which was then removed. Several cysts were found on the left ovary as well, one of which was filled with brown thick fluid.
A Uterine fibroid was found and removed after separating it from the uterus.
Neither ascites nor metastases were found.
The final pathological results were serous cystadenoma, hyalinized and necrotic with foci of endometriosis measuring 15 × 10 × 7 cm, leiomyoma measuring 1.5 × 1.3 × 1 cm (Fig. 3)
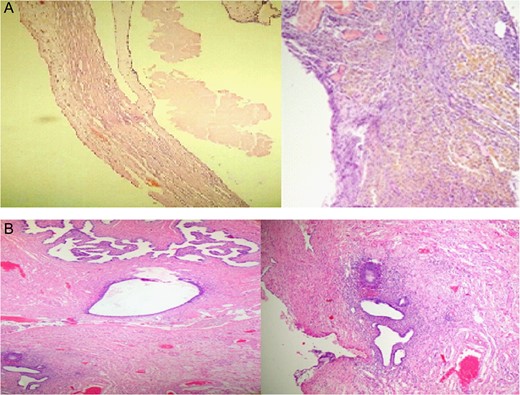
DISCUSSION
An I-131 WBS is used after total thyroidectomy to determine any residual or metastasic disease. The uptake of radioiodine by thyroid tissue is related to the expression of sodium iodide symporter (NIS). However, many cases of unexpected radioiodine uptake have been reported, explained by functional NIS in normal tissues or retention of radioiodine in body fluids and inflamed tissues [1, 2].
In our case, the patient showed high-thyroglobulin level after thyroidectomy, which indicated the first dose of radioiodine. Re-evaluation after 6 months showed persistent high-thyroglobulin level leading to a second dose. A WBS scan performed 5 days after this dose demonstrated high-radioiodine uptake in the pelvic region suggesting the diagnosis of metastasis.
Pathological study after surgery assured that neither thyroid tissue nor teratogenic tissues were found in the specimen and the final pathology diagnosis was serous cystadenoma, endometriosis cyst and leiomyoma.
In medical literature, Kim EE et al. [3], reported in 1984 a case of false-positive radioiodine uptake in a serous cystadenoma while Qiu ZL et al. [4] in 2010 reported a case of false uptake in a benign mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary.
Lungo M et al. [5] and Hannoush et al. [6] in 2000 and 2017 reported a false-positive radioiodine uptake in endometrial cyst. Benign cystadenofibroma was reported by Flug J et al. [7].
There are many reported cases of false-positive radioiodine uptake in tissues other than ovary, such as bone tissue [8], hepatic hydatid cyst [9] and parapelvic renal cyst [10].
As the real cause behind iodine uptake by these tissues leading to such false-positive results has yet to be established, our case, side by side with similar cases, may lead to a better comprehension how this issue occurs. Until that moment, careful consideration should be applied to any suspicious case (Table 2).
| . | TSH . | Thyroglobulin . | Thyroglobulin antibody . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before first radioiodine dose | 52 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 16.1 uIU/ ml (0–40 uIU/ml) |
| After first dose (3 months) | 0.1 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 18.1 uIU/ ml (0–40 uIU/ ml) |
| Before second dose (6 months) | 16.4 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | |
| After second dose and surgery (9 months) | 0.45 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | <0.2 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 27 uIU/ml (0–40 uIU/ml) |
| . | TSH . | Thyroglobulin . | Thyroglobulin antibody . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before first radioiodine dose | 52 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 16.1 uIU/ ml (0–40 uIU/ml) |
| After first dose (3 months) | 0.1 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 18.1 uIU/ ml (0–40 uIU/ ml) |
| Before second dose (6 months) | 16.4 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | |
| After second dose and surgery (9 months) | 0.45 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | <0.2 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 27 uIU/ml (0–40 uIU/ml) |
| . | TSH . | Thyroglobulin . | Thyroglobulin antibody . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before first radioiodine dose | 52 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 16.1 uIU/ ml (0–40 uIU/ml) |
| After first dose (3 months) | 0.1 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 18.1 uIU/ ml (0–40 uIU/ ml) |
| Before second dose (6 months) | 16.4 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | |
| After second dose and surgery (9 months) | 0.45 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | <0.2 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 27 uIU/ml (0–40 uIU/ml) |
| . | TSH . | Thyroglobulin . | Thyroglobulin antibody . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before first radioiodine dose | 52 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 16.1 uIU/ ml (0–40 uIU/ml) |
| After first dose (3 months) | 0.1 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 18.1 uIU/ ml (0–40 uIU/ ml) |
| Before second dose (6 months) | 16.4 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | >500 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | |
| After second dose and surgery (9 months) | 0.45 uIU/ml (0.4–4 uIU/ml) | <0.2 ng/ml (1.7–55.6 ng/ml) | 27 uIU/ml (0–40 uIU/ml) |
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
None declared.
REFERENCES
- computed tomography
- endometriosis
- heterogeneity
- papillary carcinoma
- cystadenoma, serous
- cysts
- follow-up
- iodine
- fibroid tumor
- neoplasm metastasis
- surgical procedures, operative
- syria
- thyroid diseases
- thyroidectomy
- urinary bladder
- diagnosis
- pathology
- pelvis
- surgery specialty
- thyroglobulin
- thyroid
- thyrotropin
- pelvic mass
- radioactive iodine
- iodine uptake studies
- thyroglobulin antibody measurement
- false-positive results
- excision
- participation in ward rounds
- calcification



