-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Rodrigo C. Surjan, Fabio F. Makdissi, Tiago Basseres, Marcel A.C. Machado, Enucleation of liver tumors: you do not have to feel blue about it, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2015, Issue 10, October 2015, rjv130, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjv130
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Enucleation of hepatic tumors is a low-morbidity technique with adequate oncological results that is useful in many clinical settings. Compared with anatomical liver resections, it offers the advantage of maximal hepatic parenchymal preservation. However, some technical adversities may occur during the enucleation of liver tumors, such as difficulty in finding the lesions by intraoperative ultrasonography after hepatic transection or further visually spotting the tumor within the parenchyma if a first specimen is retracted not containing the lesion. We describe an innovative technique that overcomes these possible adversities and makes the enucleation of liver tumors easier and more precise.
INTRODUCTION
Although anatomical liver resection is the standard of care for treatment of neoplastic hepatic disease (either primary or secondary), non-anatomical liver resections can still be useful in some situations. It is a low-morbidity technique that can be timely used for tumors near the hepatic surface [1]. It also has become a useful tool after widespread implementation of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for hepatic metastasis, which many times reduces lesions dimensions to small ‘scar tissue’ nodules, very suitable to non-anatomical resections [2]. Non-anatomical hepatectomy offers the advantage of preserving hepatic parenchyma when compared with segment-oriented hepatectomy, being a safe option with good oncological results in patients with chronic hepatic disease and hepatocellular carcinoma and in the setting of staged hepatectomy in patients with multiple nodules [3–5].
Despite being at first impression a very easy technique, one may face some difficulties while performing an enucleation of a tumor that is not visible at the hepatic surface. After proper localization of a small lesion with intraoperative ultrasonography and initiation of the transection of the parenchyma, the resulting bleeding and disruption of the hepatic tissue can easily make the tumor no longer visually identifiable if not recovered in the initial resected specimen, and further ultrasonography examination may not access the tumor after disruption of the hepatic tissue.
This article describes a simple, efficient and low-cost maneuver to make enucleation of hepatic lesions not visible at the hepatic surface a precise and straight to the point technique. It consists of inserting methylene blue on the lesions by ultrasonographic guidance.
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE
Based on preoperative image studies, the portion on the liver that contains the tumor is fully mobilized by transection of hepatic ligaments. Then, intraoperative ultrasonography is performed in order to achieve precise localization of the lesion and estimation of its deepness (Fig. 1).
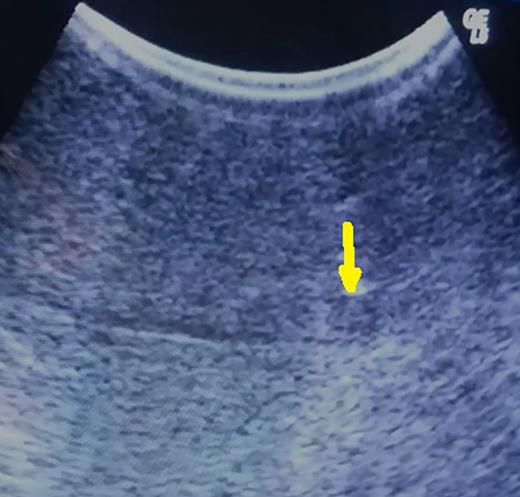
Hypoechoic 5-mm lesion at 2 cm depth (metachronous metastatic tumor from colorectal carcinoma) (arrow).
Under ultrasonography guidance, a 30-gauge needle is inserted until reaching the tumor (Fig. 2a). At this time, 5 ml of methylene blue is inserted, and the needle is retracted from the liver. The first result is that a small area around the tumor and the lesion itself will immediately change its echographic characteristics, becoming much more hyper-reflective and easily identifiable by ultrasonography (Fig. 2b).
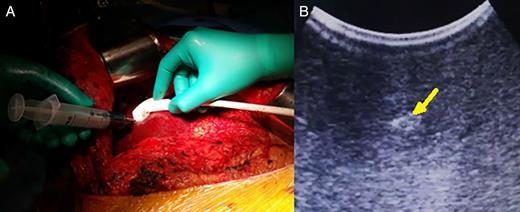
(A) Methylene blue injection under ultrasonographic guidance and (B) easily identifiable methylene blue-injected lesion with hyper-echoic pattern (arrow).
After that, Glisson's capsule is marked with cautery leaving a 2-cm margin. The area is checked again with ultrasonography just before liver transection. Usually, transection is performed with bipolar forceps.
During the transection, close to the depth previously defined, intraoperative ultrasonography is repeated, and a well-defined area containing the tumor and methylene blue will be identifiable, despite the disruption of the hepatic parenchyma (Fig. 3). Resection is completed and specimen checked to confirm the presence of the lesion inside.
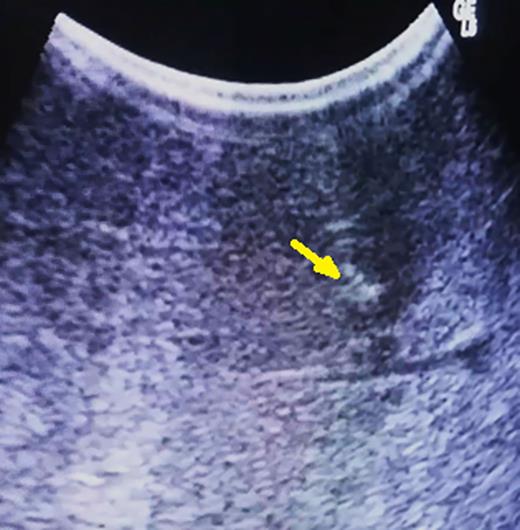
After parenchymal disruption, hyper-echoic lesion still clearly by ultrasonography (arrow).
If the tumor is not retrieved with the specimen, despite the bleeding caused by parenchymal transection, further inspection of the manipulated hepatic bed will disclose the presence of methylene blue, and under direct visualization of the area of the tumor, a second specimen is retrieved containing the lesion (Fig. 4).
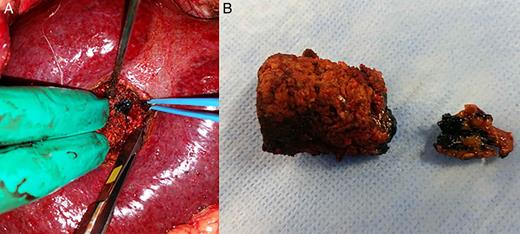
(A) Methylene blue-injected area containing the tumor within the parenchyma and (B) two specimens: the smaller one, that was displaced deeper within the parenchyma, containing the tumor.
DISCUSSION
Methylene blue is an aromatic chemical compound with many uses in biology and chemistry. It was first prepared by German chemist Heinrich Caro in 1876 and is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines as one of the most important medication needed in a basic health system [6, 7]. It is described as the first fully synthetic drug used in medicine being used in the treatment of malaria since 1891 and is largely used in many clinical situations with safety [8].
Anatomical liver resections are the recommended technique for most of the hepatic tumors. However, non-anatomical wedge resections can be effective and have good oncological results especially in small metastatic lesions and has the advantage of sparing hepatic parenchyma, that is indispensable in patients with chronic hepatic disease or with severe chemotherapy-associated liver injury and in the setting of staged hepatectomies or in patients with multiple lesions [1, 9].
During the enucleation of a hepatic tumor not visible in the hepatic surface, one may face some difficulties. After parenchymal transection, disruption of the hepatic tissue many times makes the tumor not visible any longer by repeat ultrasonography, which is often performed to check the depth of the transection. Furthermore, if the specimen is retracted and the tumor is not present, the bleeding in the cutting line makes it difficult to find the tumor within the hepatic parenchyma.
Injecting methylene blue in the tumor overcomes both difficulties cited above. The lesion becomes much more hyper-echogenic at ultrasonography even after the parenchymal transection, and the tumor injected with methylene blue presents a great deal more visual contrast with the surrounding hepatic tissue, becoming easily identifiable if a first specimen was retracted not containing the lesion.
This simple maneuver can make enucleation of hepatic tumors not visible at the hepatic surface an easier, faster and more precise maneuver. It presents the advantages of making the area of the tumor much more hyper-reflective at intraoperative ultrasonography even after hepatic transection and much more visually identifiable within the hepatic parenchyma after an initial specimen is retracted not containing the tumor and further resection is needed.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
None declared.



