-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Masahiko Narita, Tomonori Shirasaka, Ryohei Ushioda, Hiroyuki Kamiya, Triplex vascular prostheses elongation in post-operative course, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2022, Issue 6, June 2022, rjac255, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjac255
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Triplex (Terumo Corp, Tokyo, Japan) is a relatively new vascular protheses with a non-biodegradable coating material. We experienced two cases of graft elongation in Triplex grafts post-operatively. In one of the cases, the graft elongation led to occlusion of the left subclavian artery. In the other case, the graft elongation resulted in a pseudoaneurysm of the ascending aorta. A unique feature of Triplex grafts is that they may reduce post-operative inflammation reaction; however, they could also invite a limited adhesion formation with the surrounding tissue, which contribute to prostheses elongation, due to a lack of prostheses stability and fixation. A careful observation based on the feature of implanted protheses is required.
INTRODUCTION
Synthetic vascular prostheses are commonly used for open surgery for aortic aneurysms and dissections. Although the options for prosthetic products have increased with innovations, various characteristics and clinical outcome of grafts remain unclear. Triplex is a relatively new prostheses, and several studies reported its material properties and clinical benefits [1–5]. Herein, we present two cases of the Triplex graft elongation in post-operative course, which resulted in surgical reinterventions.
CASE REPORT
Case 1: A 42-year-old male underwent total arch replacement (TAR) for acute aortic dissection with Triplex vascular prosthesis (Fig. 1A). Nineteen months after the operation, the patient complained of left upper-extremity psychroesthesia and malaise. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) showed an expected elongation of the Triplex graft, resulting in the occlusion of the graft branch to left subclavian artery (Fig. 1B). A left carotid-axillary bypass was performed, which relieved the symptoms successfully.
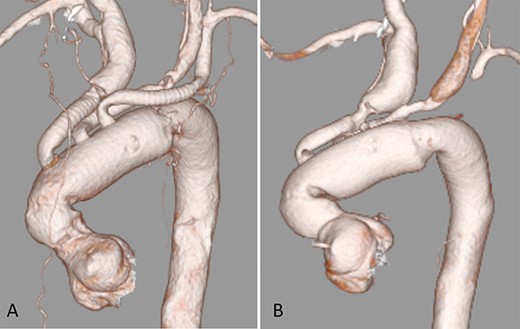
CECT 3D reconstruction; (A) after initial operation; (B) 19 months after the operation
Case 2: A 21-year-old male was experiencing post-operative aortic regurgitation and peripheral anastomotic stenosis after undergoing the David procedure and hemi-arch replacement for annuloaortic ectasia 2 years ago. His subsequent treatment included an aortic valve replacement (AVR) and TAR using a Triplex graft (Fig. 2A). Ten months post-operatively, the patient presented with acute chest pain. CECT revealed a pseudoaneurysm of the ascending aorta, which was considered to be the cause of symptoms. Furthermore, the Triplex main body was kinked due to graft elongation. This structural defect could have applied pressure on the anastomotic site, resulting in the pseudoaneurysm (Fig. 2B). In the course of conservative treatment, the pseudoaneurysm was dilated and was followed by the Bentall procedure and TAR. Intraoperative findings showed that there was no adhesion of the Triplex graft to the surrounding tissue.
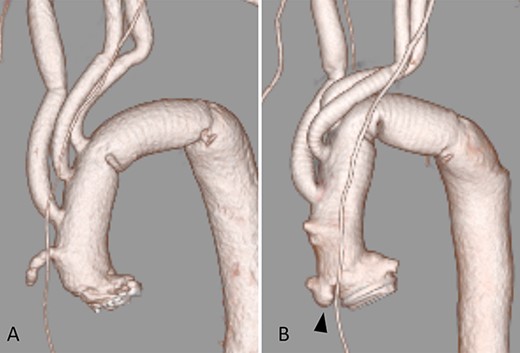
(A) After AVR and TAR; (B) 10 months after the operation; arrow shows a pseudoaneurysm of the ascending aorta
DISCUSSION
A unique feature of Triplex vascular prostheses includes the presence of a non-biodegradable coating material. However, this could result in post-operative graft elongation. Triplex grafts have a three-layered structure [1, 2]. The inner layer is an un-coated woven Dacron graft, and the outer layer is an expanded polytetrafluoroethylene graft. The middle layer is made of non-biodegradable styrene elastomer resin, which is considered to be clinically advantageous as it may reduce post-operative inflammatory response and the amount of mediastinal drainage [3–5]. However, this middle layer does not degrade biologically, potentially introducing the risk of incorporation of implanted prostheses into the surrounding tissues. Fujiwara and colleagues [6] showed that the Triplex graft exhibited less propensity for adhesion formation with the surrounding tissue in an animal study. This limited adhesion formation could contribute to prostheses elongation because of a lack of prostheses stability and fixation.
Upon experiencing post-operative vascular protheses elongation in two cases, it can be concluded that a careful observation based on the feature of implanted protheses is required.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
None declared.
FUNDING
None.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Written informed consent was obtained from the families of the patient for scientific activity, including publication of this case report.



