-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Nikolaos Papatheodorou, Anthimos Keskinis, Paraskevas Georgoulas, Konstantinos Tilkeridis, Sotirios Botaitis, Sempachedin Perente, Ioanna Kougioumtzi, Hand compartment syndrome due to extravasation of contrast medium. A technical error. A report of a case and review of the literature, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2022, Issue 3, March 2022, rjac054, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjac054
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
The extravasation of contrast agents is one of the most common and remarkable complications during a computed tomography (CT) scan. The clinical manifestations are commonly minimal, leading to mild symptoms. However, in rare cases of high-volume extravasation, the complications are extremely threatening. Compartment syndrome of the hand and the forearm leads to critical dysfunction and upper limb necrosis. This article reported an unusual case of hand compartment syndrome following extravasation of iodinated contrast agent from a peripheral venous catheter, during a CT angiography, and its surgical treatment. Moreover, a literature review regarding all published similar surgically treated cases was conducted.
INTRODUCTION
The extravasation of contrast agents is one of the most common and remarkable complications during a CT scan [1]. The clinical manifestations are commonly minimal, leading to mild symptoms. However, in rare cases of high-volume extravasation, the complications are extremely threatening [2, 3].
This article reported an unusual case of hand compartment syndrome following extravasation of iodinated contrast agent and its surgical treatment. A literature review regarding all published similar surgically treated cases is also presented.
CASE REPORT
A 79-year-old male patient was admitted to the emergency department with critical limb ischemia. A computed tomography angiography (CTA) was conducted to evaluate arterial blood flow of the right lower extremity. CTA was performed by infusion of an iodinated contrast agent through an automated power injector from a distal vein at the dorsal aspect of the right hand.
Shortly after the infusion, the patient was admitted to the surgical department complaining of acute pain on his right hand at the site of the infusion. Physical examination revealed a swollen, paleness, erythematous and tense hand with skin blistering on dorsal aspect (Fig. 1). The hand appeared warm with diminished but not absolutely absent pulses along radial and ulnar arteries, loss of superficial sensitivity and minus posturing. Fingers were also swollen, and capillary refill time was prolonged. Passive extension of the fingers was very painful. The pain remained for up to 6 h. Conservative treatment with elevation of the forearm and analgesics did not improve the clinical symptoms. Compartment syndrome (CS) was diagnosed, and 8 h post infusion the patient underwent emergent fasciotomies.
Multiple incisions of the hand and the forearm were required to decompress all involved osseofascial compartments (Fig. 2a–c). Primarily, two dorsal longitudinal incisions through second and fourth metacarpal were done in order to decompress the dorsal interosseous (×4) compartments. Dissection of the fascia was carried down along the sides of each metacarpal. The hematoma as well as fluid were also drained (Fig. 3). Deeper dissection was continued along the radial aspect of the second metacarpal to release the adductor compartment. Afterwards, two volar incisions over the thenar and hypothenar area (radial to the first metacarpal and ulnar to the fifth metacarpal, respectively) were made so as to reduce the pressure of the aforementioned compartments. Volar interosseous (×3) were also released. Digits’ compartments were additionally decompressed via ulnar longitudinal incision of each finger. Subsequently, the carpal tunnel ligament was dissected through a palmar longitudinal incision and the median nerve was decompressed. Finally, the increased forearm pressure of volar, dorsal and mobile wad (lateral) compartments was also relieved.
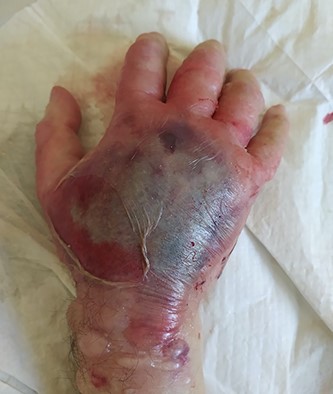
Swollen, paleness, erythematous and tense hand with skin blistering on dorsal aspect following extravasation of iodinated contrast agent.
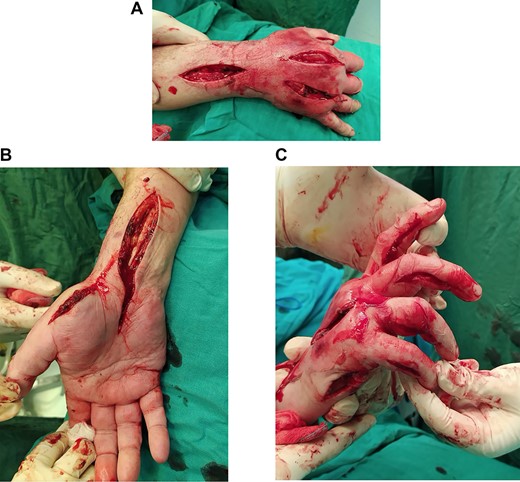
(A) Dorsal decompression of the dorsal interosseous and antebrachium compartments. (B) Thenar and carpal canal decompression. (C) Hypothenar decompression along with digit release via ulnar longitudinal incision of each finger.
Twelve papers (listed in chronological order) reporting compartment syndrome due to contrast medium extravasation at the hand and/or forearm that treated surgically
| Author . | Age . | Localization . | Contrast medium used . | Distal pulses . | Time of surgery . | Fasciotomies . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loth et al. 1988 [7] | 51 years | Hand | Renografin 76 (Diatrizoate meglumine) | N/A | 20 h | N/A |
| 40 years | Antecubital area | Mixture of Renografin 60 & 30 | N/A | 6 h | N/A | |
| 54 years | Forearm | 150 ml of 60% iothalamate rneglumine | yes | N/A | N/A | |
| 47 years | Forearm and hand | 45 ml 60% iothalamate rneglumiec | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 45 years | Forearm | 60% iothalamate rneglumin | N/A | 1 h | N/A | |
| Selek et al. 2007 [8] | 70 years | Hand | 100 ml of non-ionic iodinated contrast medium (Ultravist 300) | N/A | 8 h | Carpal tunnel, interosseous and adductor compartments |
| Grand et al. 2008 [9] | 48 years | Forearm | 53 mL of Omnipaque 350 contrast medium | Absent | 1 h | Carpal tunnel, volar and dorsal of the forearm |
| Ensat et al. 2010 [10] | 44 years | Left forearm | non-ionic iodinated contrast medium (Xenetix) | Absent | N/A | N/A |
| D'Asero et al. 2010 [3] | 81 years | Hand | 100 ml of non-ionic iodinated contrast medium | Absent | N/A | Interosseous compartments, thumb adductor |
| Belzunegui et al. 2011 [2] | 50 years | Hand | 100 ml non-ionic iodinated contrast (Optiray UltraJet 350 mg/ml) | N/A | 6 h | Interosseous compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel, thumb adductor |
| Güner et al. 2012 [11] | 48 years | Hand | 90 ml of the non-ionic water-soluble iso-osmolar contrast medium, iodixanol | asent | 3 h | Dorsal interosseous and adductor compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel |
| Altan et al. 2013 [12] | 23 days | Hand and forearm | 10 ml of iohexol Omnipaque (non-ionic) | absent | 2 h | Extended volar, carpal tunnel |
| Yurdakul et al. 2014 [13] | 60 years | Hand | 100 ml of iohexol (non-ionic) | absent | 2 h | Dorsal interosseous compartments, carpal tunnel |
| Vinod et al. 2016 [14] | 63 years | Hand | 100 ml Optiscan-300, containing iohexol | N/A | 15 h | Dorsal interosseous compartments |
| Stavrakakis et al. 2018 [15] | 72 years | Hand | 110 ml of Iopromide | N/A | 5 h | Interosseous compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel, thumb adductor |
| van Veelen et al. 2020 [5] | 43 years | Forearm | 110 ml of iomeprolum, non-ionic iodinated contrast medium | Absent | 39 min | Carpal tunnel, volar and dorsal of the forearm |
| Author . | Age . | Localization . | Contrast medium used . | Distal pulses . | Time of surgery . | Fasciotomies . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loth et al. 1988 [7] | 51 years | Hand | Renografin 76 (Diatrizoate meglumine) | N/A | 20 h | N/A |
| 40 years | Antecubital area | Mixture of Renografin 60 & 30 | N/A | 6 h | N/A | |
| 54 years | Forearm | 150 ml of 60% iothalamate rneglumine | yes | N/A | N/A | |
| 47 years | Forearm and hand | 45 ml 60% iothalamate rneglumiec | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 45 years | Forearm | 60% iothalamate rneglumin | N/A | 1 h | N/A | |
| Selek et al. 2007 [8] | 70 years | Hand | 100 ml of non-ionic iodinated contrast medium (Ultravist 300) | N/A | 8 h | Carpal tunnel, interosseous and adductor compartments |
| Grand et al. 2008 [9] | 48 years | Forearm | 53 mL of Omnipaque 350 contrast medium | Absent | 1 h | Carpal tunnel, volar and dorsal of the forearm |
| Ensat et al. 2010 [10] | 44 years | Left forearm | non-ionic iodinated contrast medium (Xenetix) | Absent | N/A | N/A |
| D'Asero et al. 2010 [3] | 81 years | Hand | 100 ml of non-ionic iodinated contrast medium | Absent | N/A | Interosseous compartments, thumb adductor |
| Belzunegui et al. 2011 [2] | 50 years | Hand | 100 ml non-ionic iodinated contrast (Optiray UltraJet 350 mg/ml) | N/A | 6 h | Interosseous compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel, thumb adductor |
| Güner et al. 2012 [11] | 48 years | Hand | 90 ml of the non-ionic water-soluble iso-osmolar contrast medium, iodixanol | asent | 3 h | Dorsal interosseous and adductor compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel |
| Altan et al. 2013 [12] | 23 days | Hand and forearm | 10 ml of iohexol Omnipaque (non-ionic) | absent | 2 h | Extended volar, carpal tunnel |
| Yurdakul et al. 2014 [13] | 60 years | Hand | 100 ml of iohexol (non-ionic) | absent | 2 h | Dorsal interosseous compartments, carpal tunnel |
| Vinod et al. 2016 [14] | 63 years | Hand | 100 ml Optiscan-300, containing iohexol | N/A | 15 h | Dorsal interosseous compartments |
| Stavrakakis et al. 2018 [15] | 72 years | Hand | 110 ml of Iopromide | N/A | 5 h | Interosseous compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel, thumb adductor |
| van Veelen et al. 2020 [5] | 43 years | Forearm | 110 ml of iomeprolum, non-ionic iodinated contrast medium | Absent | 39 min | Carpal tunnel, volar and dorsal of the forearm |
Twelve papers (listed in chronological order) reporting compartment syndrome due to contrast medium extravasation at the hand and/or forearm that treated surgically
| Author . | Age . | Localization . | Contrast medium used . | Distal pulses . | Time of surgery . | Fasciotomies . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loth et al. 1988 [7] | 51 years | Hand | Renografin 76 (Diatrizoate meglumine) | N/A | 20 h | N/A |
| 40 years | Antecubital area | Mixture of Renografin 60 & 30 | N/A | 6 h | N/A | |
| 54 years | Forearm | 150 ml of 60% iothalamate rneglumine | yes | N/A | N/A | |
| 47 years | Forearm and hand | 45 ml 60% iothalamate rneglumiec | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 45 years | Forearm | 60% iothalamate rneglumin | N/A | 1 h | N/A | |
| Selek et al. 2007 [8] | 70 years | Hand | 100 ml of non-ionic iodinated contrast medium (Ultravist 300) | N/A | 8 h | Carpal tunnel, interosseous and adductor compartments |
| Grand et al. 2008 [9] | 48 years | Forearm | 53 mL of Omnipaque 350 contrast medium | Absent | 1 h | Carpal tunnel, volar and dorsal of the forearm |
| Ensat et al. 2010 [10] | 44 years | Left forearm | non-ionic iodinated contrast medium (Xenetix) | Absent | N/A | N/A |
| D'Asero et al. 2010 [3] | 81 years | Hand | 100 ml of non-ionic iodinated contrast medium | Absent | N/A | Interosseous compartments, thumb adductor |
| Belzunegui et al. 2011 [2] | 50 years | Hand | 100 ml non-ionic iodinated contrast (Optiray UltraJet 350 mg/ml) | N/A | 6 h | Interosseous compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel, thumb adductor |
| Güner et al. 2012 [11] | 48 years | Hand | 90 ml of the non-ionic water-soluble iso-osmolar contrast medium, iodixanol | asent | 3 h | Dorsal interosseous and adductor compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel |
| Altan et al. 2013 [12] | 23 days | Hand and forearm | 10 ml of iohexol Omnipaque (non-ionic) | absent | 2 h | Extended volar, carpal tunnel |
| Yurdakul et al. 2014 [13] | 60 years | Hand | 100 ml of iohexol (non-ionic) | absent | 2 h | Dorsal interosseous compartments, carpal tunnel |
| Vinod et al. 2016 [14] | 63 years | Hand | 100 ml Optiscan-300, containing iohexol | N/A | 15 h | Dorsal interosseous compartments |
| Stavrakakis et al. 2018 [15] | 72 years | Hand | 110 ml of Iopromide | N/A | 5 h | Interosseous compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel, thumb adductor |
| van Veelen et al. 2020 [5] | 43 years | Forearm | 110 ml of iomeprolum, non-ionic iodinated contrast medium | Absent | 39 min | Carpal tunnel, volar and dorsal of the forearm |
| Author . | Age . | Localization . | Contrast medium used . | Distal pulses . | Time of surgery . | Fasciotomies . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loth et al. 1988 [7] | 51 years | Hand | Renografin 76 (Diatrizoate meglumine) | N/A | 20 h | N/A |
| 40 years | Antecubital area | Mixture of Renografin 60 & 30 | N/A | 6 h | N/A | |
| 54 years | Forearm | 150 ml of 60% iothalamate rneglumine | yes | N/A | N/A | |
| 47 years | Forearm and hand | 45 ml 60% iothalamate rneglumiec | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 45 years | Forearm | 60% iothalamate rneglumin | N/A | 1 h | N/A | |
| Selek et al. 2007 [8] | 70 years | Hand | 100 ml of non-ionic iodinated contrast medium (Ultravist 300) | N/A | 8 h | Carpal tunnel, interosseous and adductor compartments |
| Grand et al. 2008 [9] | 48 years | Forearm | 53 mL of Omnipaque 350 contrast medium | Absent | 1 h | Carpal tunnel, volar and dorsal of the forearm |
| Ensat et al. 2010 [10] | 44 years | Left forearm | non-ionic iodinated contrast medium (Xenetix) | Absent | N/A | N/A |
| D'Asero et al. 2010 [3] | 81 years | Hand | 100 ml of non-ionic iodinated contrast medium | Absent | N/A | Interosseous compartments, thumb adductor |
| Belzunegui et al. 2011 [2] | 50 years | Hand | 100 ml non-ionic iodinated contrast (Optiray UltraJet 350 mg/ml) | N/A | 6 h | Interosseous compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel, thumb adductor |
| Güner et al. 2012 [11] | 48 years | Hand | 90 ml of the non-ionic water-soluble iso-osmolar contrast medium, iodixanol | asent | 3 h | Dorsal interosseous and adductor compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel |
| Altan et al. 2013 [12] | 23 days | Hand and forearm | 10 ml of iohexol Omnipaque (non-ionic) | absent | 2 h | Extended volar, carpal tunnel |
| Yurdakul et al. 2014 [13] | 60 years | Hand | 100 ml of iohexol (non-ionic) | absent | 2 h | Dorsal interosseous compartments, carpal tunnel |
| Vinod et al. 2016 [14] | 63 years | Hand | 100 ml Optiscan-300, containing iohexol | N/A | 15 h | Dorsal interosseous compartments |
| Stavrakakis et al. 2018 [15] | 72 years | Hand | 110 ml of Iopromide | N/A | 5 h | Interosseous compartments, thenar, hypothenar, carpal tunnel, thumb adductor |
| van Veelen et al. 2020 [5] | 43 years | Forearm | 110 ml of iomeprolum, non-ionic iodinated contrast medium | Absent | 39 min | Carpal tunnel, volar and dorsal of the forearm |
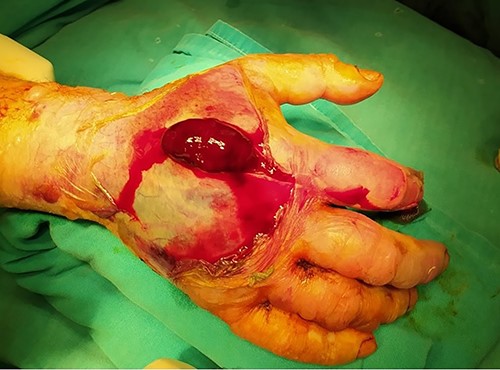
The patient’s post-surgery clinical appearance was gradually improved. Five days after decompression, the patient returned to the theater and underwent a delayed wound primary closure (Fig. 4a and b). At the last follow-up, 2 months after the surgery, the patient had retrieved full range of motion of the wrist joint and the fingers. The wounds were healed adequately and the possible risk of upper limb necrosis and dysfunction was overcome.
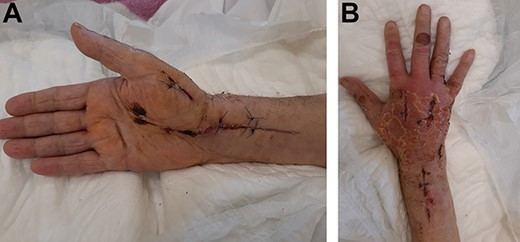
(A) Twenty-day postoperative view of the hand with tension-free skin closure. (B) Twenty-day postoperative view of the hand with tension-free skin closure.
DISCUSSION
According to literature, extravasation can be frequently observed in infants, young children, unconscious patients, elderly or frail patients with fragile blood vessels or patients receiving chemotherapy. More severe extravasation injuries observed in patients with low muscular mass and atrophic subcutaneous tissue. Arterial or venous insufficiency as well as compromised lymphatic drainage could also lead to extravasation of contrast medium in the subcutaneous tissue during the infusion procedure [1].
Large volume extravasation, commonly defined as a quantity over 50 ml, as well as the usage of an automated power injector pump can cause severe skin ulceration and necrosis [2]. The type of venous access affects the frequency of extravasation. Extravasation injury is frequently associated with injection into the dorsum of the hand or the foot [1]. Across the recent literature there have been reported 16 similar cases (Table 1) who experienced CS due to contrast medium (non-ionic iodinated) extravasation at hand and/or forearm that needed urgent fasciotomy in order to avoid irreversible complications of the limb.
In our case we used an automated power injector and a high osmolar contrast medium (Scanlux 300 mg/ml, iopamidol) in an elderly patient with a documented past medical history of arterial insufficiency. The infusion was made through a distal vein at the dorsal aspect of the right hand. Therefore, the error that was detected in our case was an inadequate intravenous access site in a patient with high risk of vessel rupture. In order to reduce the risk of contrast extravasation injury we could use contrast agents with low osmolality (iopamidol) through larger veins at the antecubital fossa.
The diagnosis of acute CS is mainly clinical. The 5Ps’ rule (pain, paresthesias, paralysis, pallor and pulselessness), as well as palpable fullness, presence of blisters, erethymatous or dusky hue are findings that lead to a clinical diagnosis consistent with the CS. Apart from pain, the remaining appear as late findings [1, 3, 4].
According to Mandlik et al. [4] all the aforementioned clinical findings suggest severe injury and, in some cases, necessitate early referral to (plastic) surgeon consultation. The treatment of extravasation injuries should be described as conservative. It is not possible to predict whether the extravasation injury will resolve naturally or will result in necrosis, ulceration or permanent soft tissue injury [1]. Another treatment option for prevention of CS is the so-called ‘wash out’ technique [1, 4, 5].
According to Rubinstein et al. emergency fasciotomy is used as last attempt to treat acute CS. This therapeutic process should be performed as soon as possible, preferably within the first 6 h, in order to relieve neurovascular compromise and prevent further deterioration [6].
CONCLUSION
We should always be aware of this extremely threatening complication, so early identification is of paramount importance in order to reduce the risk of irreversible ischemia of the hand. We should also keep in mind an early plastic surgeon or hand surgeon consultation for evaluation of all extravasation events that develop symptoms of CS of the hand, regardless of the volume of the extravasation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
None declared.



