-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Daniele Scoglio, Maurizia Pozzobon, Mauro Battistioli, Gianni Bonotto, Vincenzo Caronia, Orlando Gualandi, Paolo Callegari, Asymptomatic pneumoperitoneum or pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis? Easy to make a mistake, Journal of Surgical Case Reports, Volume 2021, Issue 4, April 2021, rjab138, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjab138
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Pneumoperitoneum refers to the presence of intraperitoneal free gas outside the viscera. A perforation of a hollow viscus is the main cause and usually indicates a surgical emergency. However, some case of pneumoperitoneum can be completely asymptomatic and secondary to benign conditions that do not require any surgical intervention. In this situation a misleading diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum may occur. The authors are going to present a case of a 79-year-old man with an asymptomatic pneumoperitoneum incidentally detected by CT-scan and subsequently revealed to be pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis (PCI) at diagnostic laparoscopy. PCI is a rare condition characterized by the presence of gas-filled cyst in the submucosa/subserosa of the bowel wall that can easily mimic pneumoperitoneum on radiological imaging. A thorough examination of radiological findings is crucial in preventing unnecessary surgical procedures that may expose patients to potential associated morbidities.
INTRODUCTION
Pneumoperitoneum refers to the presence of free gas in the peritoneal cavity. A visceral perforation accounts for 85 to 95% of all cases and generally indicates a surgical emergency [1]. However, in about 10% of cases a variety of benign conditions could also determine a spontaneous pneumoperitoneum that do not require any surgical intervention (Table 1) [2]. In these cases, pneumoperitoneum is frequently asymptomatic and incidentally detected by radiological investigations. Sometimes, CT-scan may also reveal a false imaging of free intraperitoneal air determining a misleading diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum. The authors are going to present one of these cases turned out to be PCI at the diagnostic laparoscopy. Our objective is to stress the importance of a prompt recognition of nonsurgical pneumoperitoneum.
CASE REPORT
This is a case of a 79-year-old man who underwent contrast-enhanced Brain-CT for loss of consciousness. Past medical history included diverticular disease, COPD, hypertension, atrial fibrillation and appendectomy. Of note, he had no prior history of endoscopic procedures or recent trauma. The CT showed a primary cerebral mass at the temporal right site suspected for a glioblastoma. Hence, he went through a contrast-enhanced Chest/Abdomen CT for staging. No secondary lesions were detected but a small amount of free gas was unexpectedly noted in the abdomen secondary to a suspected colonic diverticular perforation (Fig. 1). Therefore, a surgical consultation was granted. At a first observation the patient was totally asymptomatic. Vital signs were in range. He had a healthy appetite, bowel sounds were active and he was opening his bowels normally. On examination the abdomen was soft and nontender with no distension. Laboratory tests were also normal including WCC (4.72 × 103/μl) and CRP (2.05 mg/dl). To confirm the diagnosis we proposed an explorative laparoscopy that the patient refused as he was feeling well. Few weeks later he underwent neurosurgical intervention and the cerebral mass was resected. The postoperative period was uneventful and he was discharged home on postoperative Day 7.
| Abdominal |
| Post laparotomy/laparoscopy |
| Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis |
| Endoscopy |
| Peritoneal dialysis/paracentesis |
| Thoracic |
| Invasive ventilation |
| Cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| Pneumothorax |
| Pneumomediastinum |
| Barotrauma |
| Gynecological |
| Pelvic endoscopy/radiography |
| Intercourse |
| Pelvic inflammatory disease |
| Pelvic examination |
| Vaginal douching |
| Abdominal |
| Post laparotomy/laparoscopy |
| Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis |
| Endoscopy |
| Peritoneal dialysis/paracentesis |
| Thoracic |
| Invasive ventilation |
| Cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| Pneumothorax |
| Pneumomediastinum |
| Barotrauma |
| Gynecological |
| Pelvic endoscopy/radiography |
| Intercourse |
| Pelvic inflammatory disease |
| Pelvic examination |
| Vaginal douching |
| Abdominal |
| Post laparotomy/laparoscopy |
| Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis |
| Endoscopy |
| Peritoneal dialysis/paracentesis |
| Thoracic |
| Invasive ventilation |
| Cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| Pneumothorax |
| Pneumomediastinum |
| Barotrauma |
| Gynecological |
| Pelvic endoscopy/radiography |
| Intercourse |
| Pelvic inflammatory disease |
| Pelvic examination |
| Vaginal douching |
| Abdominal |
| Post laparotomy/laparoscopy |
| Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis |
| Endoscopy |
| Peritoneal dialysis/paracentesis |
| Thoracic |
| Invasive ventilation |
| Cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| Pneumothorax |
| Pneumomediastinum |
| Barotrauma |
| Gynecological |
| Pelvic endoscopy/radiography |
| Intercourse |
| Pelvic inflammatory disease |
| Pelvic examination |
| Vaginal douching |
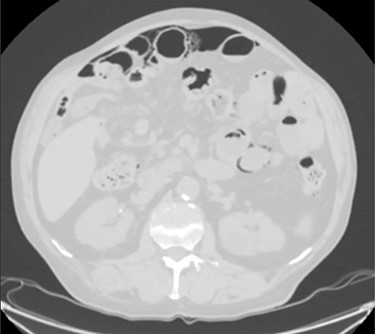
A moderate amount of intraperitoneal gas is present anteriorly to the small bowel.
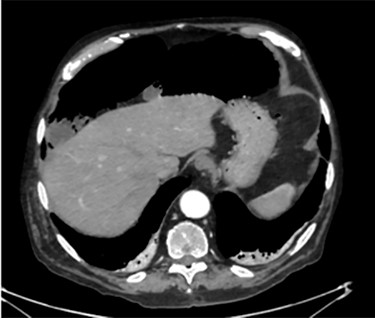
Unfortunately, once he returned home his temperature started to rise up to 38°C and he was readmitted to the hospital. A new contrast-enhanced Chest/Abdomen CT showed a bilateral pneumonia and a massive amount of intraperitoneal free gas, mainly in the abdominal upper quadrants (Fig. 2). No fat stranding, nondilated bowel, no vascular abnormalities and no free fluid were detected. Although the CT showed an evident worsening, the patient still remained completely asymptomatic on physical examination. Accordingly, he started to be treated with meropenem for pneumonia (Escherichia coli was isolated into the sputum) and he finally agreed to underwent diagnostic laparoscopy. Surprisingly, that was definitely not a case of pneumoperitoneum but an idiopathic PCI as we found multiple intramural air content cyst, about 2–3 cm in diameter, all around the small bowel loops and mesentery (Fig. 3). No intra-abdominal maneuvers were made. The patient had an unremarkable recovery (Clavien–Dindo classification grade was 1) [3] and he was discharged home on postoperative Day 15 in well condition, once he had recovered from pneumonia.
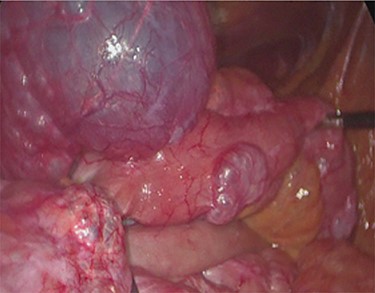
Intra-operatory findings of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis of the small bowel.
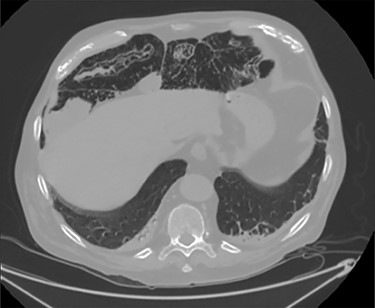
PCI was ultimately identified retrospectively using lung window settings.
DISCUSSION
PCI first documented by Du Vernoy in 1783 [4] refers to the intraoperative or radiological findings of intramural gas-filled cysts in the bowel wall (Fig. 4). PCI can easily mimic pneumoperitoneum on radiological imaging as CT, being a very sensitive examination, may show even minimal circumferential gas collections outside the bowel lumen or misrepresent some findings [5]. Liu et al. [6] found that PCI was misdiagnosed as a surgical abdomen in up to 27% of cases resulting in unnecessary operation. It is important to differentiate idiopathic PCI with a secondary form of this condition known as pneumatosis intestinalis which is not in fact a disease but a rare finding characterized by the presence of gas in the submucosal and/or subserosal of the bowel wall that may result from an underlying pathological process (Table 2). PCI has a reported incidence in general population of 0.03% on autopsy series and up to 0.37% in CT series. Its prevalence is still unknown [7]. However, Adachi et al. [8] in a retrospective, single-center study found 24.7% of PCI cases in the selected group affected by pneumoperitoneum. PCI involves most commonly the small and large bowel (respectively 42% and 36% of cases; in 22% is concomitantly present), but could also involve the mesentery and omentum [7]. Physiopathology remains still unclear although some hypotheses have been proposed such as: the ‘mechanical theory’ where an increased pressure of intraluminal gas secondary to mechanical problems breach the mucosal or serosal layers (i.e. blunt trauma, persistent vomiting, ileus or endoscopy); the ‘bacterial theory’ where an excess of intraluminal bacterial production of nitrogen gas diffuse through the bowel wall; the ‘chemical theory’ where malnutrition can prevent the digestion of carbohydrates and increased bacterial fermentation in the intestine; the ‘pulmonary theory’ that refers to increased intraluminal bowel pressure due to the respiratory system [9].
| Benign causes . | Life-threatening causes . |
|---|---|
| Iatrogenic | Intestinal ischemia |
| Surgical anastomosis | Mesenteric vascular disease |
| Endoscopy | Enteritis |
| Jejunoileal bypass | Toxic megacolon |
| Jejunostomy tubes | Volvulus |
| Infectious | Malrotation |
| Viruses—HIV, CMV, Rotavirus | Intussusception |
| Bacteria—Clostridium difficile and klebsiella | Blunt abdominal trauma |
| Cryptosporidium | |
| Inflammatory | |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | |
| Appendicitis | |
| Diverticular disease | |
| Systemic disease | |
| Sclerodermia | |
| Systemic lupus | |
| Others | |
| Psuedo-obstruction | |
| Drug induced | |
| Pulmonary disease | |
| Graft-versus-host disease | |
| Idiopathic (primary) |
| Benign causes . | Life-threatening causes . |
|---|---|
| Iatrogenic | Intestinal ischemia |
| Surgical anastomosis | Mesenteric vascular disease |
| Endoscopy | Enteritis |
| Jejunoileal bypass | Toxic megacolon |
| Jejunostomy tubes | Volvulus |
| Infectious | Malrotation |
| Viruses—HIV, CMV, Rotavirus | Intussusception |
| Bacteria—Clostridium difficile and klebsiella | Blunt abdominal trauma |
| Cryptosporidium | |
| Inflammatory | |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | |
| Appendicitis | |
| Diverticular disease | |
| Systemic disease | |
| Sclerodermia | |
| Systemic lupus | |
| Others | |
| Psuedo-obstruction | |
| Drug induced | |
| Pulmonary disease | |
| Graft-versus-host disease | |
| Idiopathic (primary) |
| Benign causes . | Life-threatening causes . |
|---|---|
| Iatrogenic | Intestinal ischemia |
| Surgical anastomosis | Mesenteric vascular disease |
| Endoscopy | Enteritis |
| Jejunoileal bypass | Toxic megacolon |
| Jejunostomy tubes | Volvulus |
| Infectious | Malrotation |
| Viruses—HIV, CMV, Rotavirus | Intussusception |
| Bacteria—Clostridium difficile and klebsiella | Blunt abdominal trauma |
| Cryptosporidium | |
| Inflammatory | |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | |
| Appendicitis | |
| Diverticular disease | |
| Systemic disease | |
| Sclerodermia | |
| Systemic lupus | |
| Others | |
| Psuedo-obstruction | |
| Drug induced | |
| Pulmonary disease | |
| Graft-versus-host disease | |
| Idiopathic (primary) |
| Benign causes . | Life-threatening causes . |
|---|---|
| Iatrogenic | Intestinal ischemia |
| Surgical anastomosis | Mesenteric vascular disease |
| Endoscopy | Enteritis |
| Jejunoileal bypass | Toxic megacolon |
| Jejunostomy tubes | Volvulus |
| Infectious | Malrotation |
| Viruses—HIV, CMV, Rotavirus | Intussusception |
| Bacteria—Clostridium difficile and klebsiella | Blunt abdominal trauma |
| Cryptosporidium | |
| Inflammatory | |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | |
| Appendicitis | |
| Diverticular disease | |
| Systemic disease | |
| Sclerodermia | |
| Systemic lupus | |
| Others | |
| Psuedo-obstruction | |
| Drug induced | |
| Pulmonary disease | |
| Graft-versus-host disease | |
| Idiopathic (primary) |
Some reports also revealed associations of PCI with chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, connective tissue disease, immunosuppression and organ transplant [2]. Clinically, PCI is asymptomatic and harmless at diagnosis and it is incidentally revealed during endoscopy, imaging examination or surgery [9]. In a small number of patients PCI may present mild symptoms such as abdominal discomfort, diarrhea and hematochezia [10]. PCI has no need for surgical intervention and can be safely managed conservatively by a wait-and-see approach, bowel rest and sometimes oxygen administration [11].
However, due to difficulties in distinguishing PCI from perforated viscus and necrotizing enterocolitis, a large percentage of patients still unnecessarily receive operative intervention. Surgery should be instead reserved for management of pneumatosis intestinalis secondary to life-threatening conditions that account for about 3% of all cases [9, 12]. To date there has been no randomized controlled trial and only few systematic reviews that specifically analyze PCI [5, 11].
CONCLUSION
This case highlights the importance of careful consideration between patient’s symptoms and radiological findings in the diagnostic and therapeutic approach to pneumoperitoneum. Surgeons have to consider all the potential causes of nonsurgical pneumoperitoneum in their decision-making process prior to decide for surgery. Recognition of the potential for nonsurgical pneumoperitoneum is important in preventing unnecessary surgical procedures that expose patients to infection, complications and extended recovery periods.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
No conflict of interest.
FUNDING
None.



