-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
William Spooner, Ken Youens-Clark, Daniel Staines, Doreen Ware, GrameneMart: the BioMart data portal for the Gramene project, Database, Volume 2012, 2012, bar056, https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bar056
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Gramene is a well-established resource for plant comparative genome analysis. Data are generated through automated and curated analyses and made available through web interfaces such as GrameneMart. The Gramene project was an early adopter of the BioMart software, which remains an integral and well-used component of the Gramene website. BioMart accessible data sets include plant gene annotations, plant variation catalogues, genetic markers, physical mapping entities, public DNA/mRNA sequences of various types and curated quantitative trait loci for various species.
Database URL:http://www.gramene.org/biomart/martview
Project description
The Gramene project (http://www.gramene.org) was launched in March 2001 as a curated, open-source, Web-accessible data resource for comparative genome analysis (1). Gramene's purpose is to provide added value to data sets available within the public sector, which facilitate researchers’ ability to understand plant genomes and take advantage of genomic sequence known in one species for identifying and understanding corresponding genes, pathways and phenotypes in other grass species. This is achieved by building automated and curated relationships between species that can be queried and displayed using web-based interfaces such as GrameneMart.
In the 10 years since its release, the Gramene database has increased in scope and scale. The 34th build released in October 2011 hosts 49M genetic markers and associated DNA sequences from hundreds of plant species, and 22 assembled plant genomes (14 completed and 8 partial). Figure 1 shows the growth of the Gramene database in numbers of complete and partially sequenced species represented in Gramene's genomes module.
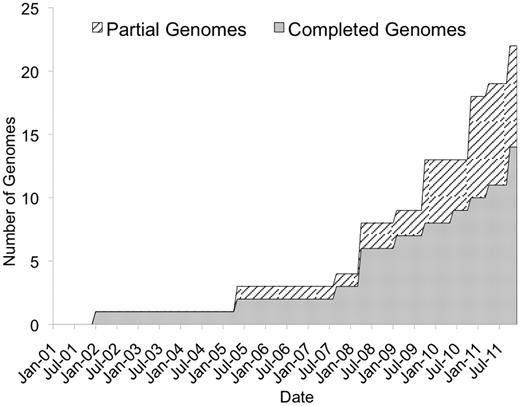
Growth in the number of species represented in Gramene's genomes module.
Alongside code developed at Gramene, the project has since January 2002 used code developed by the Ensembl project (2) for the genome browser. Gramene's first release including BioMart software (3) was version 18 in July 2005, which used the data transformation tools provided by Ensembl.
With the launch of the Ensembl Genomes project in 2009 (4), Gramene has entered into a close collaboration over the generation of plant Ensembl databases, including the sharing of Plants Genes and Plants Variations BioMarts; these databases, and the interfaces used to query them, are mirrored at both Gramene and Ensembl Genomes websites. The first coordinated release was Gramene v30, Ensembl Genomes release 3 in October 2009.
For the October 2011 release of Gramene, v34, GrameneMart was built with BioMart version 0.7 software, and the Gramene website was using BioMart version 0.7 software.
Query examples
The MartView web interface for GrameneMart is found at http://www.biomart.org/biomart/martview, with access also available from the central BioMart portal http://www.biomart.org/biomart/martview. Mirrors of the Plants Genes Mart and Plants Variations Mart are available through Ensembl Genomes; http://plants.ensembl.org/biomart/martview.
To demonstrate various features of the GrameneMart database we present various example queries in Table 1.
| Database . | Data set . | Filters . | Attributes . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query 1: Find the A. thaliana genes with orthologs in grape, the EntrezGene IDs of the grape orthologs, and the degree of homology | |||
| Plants Genes | 1. Arabidopsis thaliana genes | 1.a. MULTI SPECIES COMPARISONS: homolog filters: orthologous Vitis vinifera Genes: only |
|
| 2. Vitis vinifera genesa |
| ||
| Query 2: Which stop codon-introducing SNPs in Arabidopsis thaliana are associated with scorable phenotypes, and with what probability? | |||
| Plants Variations | 1. Arabidopsis thaliana variations |
|
|
| Query 3: List all sorghum RFLP markers and their associated GenBank sequences | |||
| Gramene Markers | 1. RFLP markers |
|
|
| Query 4: List all clones and their locations on the Maize chromosome-anchored Finger Print Contig (FPC) map from 2006. | |||
| Gramene Mappings | 1. Physical mappings |
|
|
| Query 5: Which rice QTL are associated with phenotypes related to yield? | |||
| Gramene QTL | 1. qtl |
|
|
| Database . | Data set . | Filters . | Attributes . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query 1: Find the A. thaliana genes with orthologs in grape, the EntrezGene IDs of the grape orthologs, and the degree of homology | |||
| Plants Genes | 1. Arabidopsis thaliana genes | 1.a. MULTI SPECIES COMPARISONS: homolog filters: orthologous Vitis vinifera Genes: only |
|
| 2. Vitis vinifera genesa |
| ||
| Query 2: Which stop codon-introducing SNPs in Arabidopsis thaliana are associated with scorable phenotypes, and with what probability? | |||
| Plants Variations | 1. Arabidopsis thaliana variations |
|
|
| Query 3: List all sorghum RFLP markers and their associated GenBank sequences | |||
| Gramene Markers | 1. RFLP markers |
|
|
| Query 4: List all clones and their locations on the Maize chromosome-anchored Finger Print Contig (FPC) map from 2006. | |||
| Gramene Mappings | 1. Physical mappings |
|
|
| Query 5: Which rice QTL are associated with phenotypes related to yield? | |||
| Gramene QTL | 1. qtl |
|
|
Notes: labels on the GrameneMart interface may change from release to release. The labels presented were correct for Gramene release 34 (October 2011).
aTo add the second data set to the query, follow the second ‘Dataset’ link in the left-hand panel of the interface and select from the ‘-CHOOSE ADDITIONAL DATASET-’ options.
| Database . | Data set . | Filters . | Attributes . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query 1: Find the A. thaliana genes with orthologs in grape, the EntrezGene IDs of the grape orthologs, and the degree of homology | |||
| Plants Genes | 1. Arabidopsis thaliana genes | 1.a. MULTI SPECIES COMPARISONS: homolog filters: orthologous Vitis vinifera Genes: only |
|
| 2. Vitis vinifera genesa |
| ||
| Query 2: Which stop codon-introducing SNPs in Arabidopsis thaliana are associated with scorable phenotypes, and with what probability? | |||
| Plants Variations | 1. Arabidopsis thaliana variations |
|
|
| Query 3: List all sorghum RFLP markers and their associated GenBank sequences | |||
| Gramene Markers | 1. RFLP markers |
|
|
| Query 4: List all clones and their locations on the Maize chromosome-anchored Finger Print Contig (FPC) map from 2006. | |||
| Gramene Mappings | 1. Physical mappings |
|
|
| Query 5: Which rice QTL are associated with phenotypes related to yield? | |||
| Gramene QTL | 1. qtl |
|
|
| Database . | Data set . | Filters . | Attributes . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query 1: Find the A. thaliana genes with orthologs in grape, the EntrezGene IDs of the grape orthologs, and the degree of homology | |||
| Plants Genes | 1. Arabidopsis thaliana genes | 1.a. MULTI SPECIES COMPARISONS: homolog filters: orthologous Vitis vinifera Genes: only |
|
| 2. Vitis vinifera genesa |
| ||
| Query 2: Which stop codon-introducing SNPs in Arabidopsis thaliana are associated with scorable phenotypes, and with what probability? | |||
| Plants Variations | 1. Arabidopsis thaliana variations |
|
|
| Query 3: List all sorghum RFLP markers and their associated GenBank sequences | |||
| Gramene Markers | 1. RFLP markers |
|
|
| Query 4: List all clones and their locations on the Maize chromosome-anchored Finger Print Contig (FPC) map from 2006. | |||
| Gramene Mappings | 1. Physical mappings |
|
|
| Query 5: Which rice QTL are associated with phenotypes related to yield? | |||
| Gramene QTL | 1. qtl |
|
|
Notes: labels on the GrameneMart interface may change from release to release. The labels presented were correct for Gramene release 34 (October 2011).
aTo add the second data set to the query, follow the second ‘Dataset’ link in the left-hand panel of the interface and select from the ‘-CHOOSE ADDITIONAL DATASET-’ options.
Data content
There are five BioMart databases in Gramene; Plants Genes Mart, Plants Variations Mart, Gramene Markers, Gramene Mappings and Gramene QTL. Of these, the two Plants Marts are developed with and mirrored by Ensembl Genomes, whereas the three others, Gramene Markers, Gramene Mappings and Gramene QTL, are unique to Gramene. Each database is described below.
Plant Gene Mart database
As of October 2011, Gramene's version of the Plants Genes Mart database holds a data set for each of the 14 fully sequenced plant genomes represented in Gramene. One useful feature of the Plant Genes database is the ability to map gene identifiers of one type to those of another using the extensive set of gene-anchored cross-references. Cross-reference sources from the Plant Gene Mart include EMBL (5), EntrezGene (6), IPI (7), PDB (8), RefSeq (9), UniProt (10) and UniGene (11), PlantGDB transcript assemblies (12) and identifiers from The Gene Index (13). There are also a number of species-specific identifiers, including BGI-RIS (14), the Rice Genome Annotation Project (15) and RAP-DB (16) gene identifiers for rice; IGGP (17) gene identifiers for grape; JGI gene identifiers for Arabidopsis lyrata (18), sorghum (19) and poplar (20); and TAIR (21) identifiers for Arabidopsis thaliana.
Cross-references to other Gramene modules, such as Genes, Markers/Sequences (see below) and Pathways (1) are also represented and are used to make other gene assignments to EC Number and terms from various ontologies including the Plant Ontology and Gene Ontology (22).
The Plant Gene Mart allows users to filter by, and export attributes related to, genomic region, gene biotype, database cross references, ontology terms, orthology relationships with genes in other species or paralogy with genes in the same species, protein domain annotation and, where available, consequences of any underlying genomic variants. An example query against the Plant Gene Mart database is included as ‘Query 1’ in Table 1.
Plant Variation Mart database
The Plant Variation Mart database holds a catalogue of DNA variants including single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertions/deletions (indels) for A. thaliana, rice (Japonica Group), rice (Indica Group) and grape. The A. thaliana data set contains over 8 700 000 variants compiled from a number of studies (23,24), representing SNP discovery and genotyping across over 1000 Arabidopsis accessions. In addition to the variants, their genomic locations and corresponding genetic consequences, a number of trait association data (23) are also exposed. The rice data sets, both Indica and Japonica, contain approx. 5 500 000 variants, predominantly from dbSNP (25), but also 150 000 SNPs discovered in 20 accessions by OryzaSNP (26) and data from a 1536 SNP panel genotyped across 395 accessions (27). The grape variation data set contains 460 000 SNPs discovered by next-generation sequencing of 18 grape cultivars (28).
The Plant Variation Mart allows users to filter by, and export attributes related to, genomic region, variation ID, phenotype association, variation set/study, strain/accession, gene association and consequence. An example query against the Plant Variation Mart database is included as ‘Query 2’ in Table 1.
Gramene Markers database
This database contains all of the genetic marker and associated DNA/mRNA sequence records represented in Gramene, which number 49M entries as of October 2011. Unlike the Gene and Variation Mart databases that aim to be comprehensive catalogues for their respective genomes, the Markers database represents a wide range of entities from many species that have been made available in the public domain, e.g. through databases such as GenBank.
Entities in the Gramene Markers database are classified by type, with a data set created for each type. The different types and the numbers of each are shown in Table 2. Markers are connected to each other via correspondences, e.g. individual Expressed Sequence Tags correspond to EST Clusters of which they are members, and these associations are represented in the database and exposed as filters/attributes. The database also represents groupings of markers within a type into libraries.
Marker types and number of records of each represented as data sets in the Gramene Markers biomart database
| Marker type/BioMart data set . | Number of records . |
|---|---|
| Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism, AFLP | 8150 |
| Breakpoint interval | 303 |
| Centromere | 57 |
| Clone | 2 242 577 |
| Deletion | 333 |
| EST cluster | 6 154 296 |
| Expressed sequence Tag, EST | 20 690 805 |
| Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization, FISH, Probes. | 37 |
| Fingerprint Contig, FPC | 17 479 |
| Genome Survey Sequence, GSS | 10 653 993 |
| Gene prediction | 354 564 |
| Gene | 10 781 |
| Genomic DNA | 5 263 129 |
| Insertion Site-Based Polymorphism, ISBP | 691 |
| Insertion | 310 |
| Microarray probe | 260 656 |
| mRNA | 651 207 |
| Overgo hybridization probe | 24 464 |
| Oligonucleotide | 2 396 466 |
| Point | 332 |
| Primer | 80 555 |
| Probed site | 11 532 |
| Quantitative Trait Locus, QTL | 11 625 |
| Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA, RAPD | 175 |
| Restriction fragment length polymorphism | 18 761 |
| Simple Sequence Repeat, SSR | 24 422 |
| Sequence Tagged Site, STS | 3437 |
| Telomere | 20 |
| Marker type/BioMart data set . | Number of records . |
|---|---|
| Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism, AFLP | 8150 |
| Breakpoint interval | 303 |
| Centromere | 57 |
| Clone | 2 242 577 |
| Deletion | 333 |
| EST cluster | 6 154 296 |
| Expressed sequence Tag, EST | 20 690 805 |
| Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization, FISH, Probes. | 37 |
| Fingerprint Contig, FPC | 17 479 |
| Genome Survey Sequence, GSS | 10 653 993 |
| Gene prediction | 354 564 |
| Gene | 10 781 |
| Genomic DNA | 5 263 129 |
| Insertion Site-Based Polymorphism, ISBP | 691 |
| Insertion | 310 |
| Microarray probe | 260 656 |
| mRNA | 651 207 |
| Overgo hybridization probe | 24 464 |
| Oligonucleotide | 2 396 466 |
| Point | 332 |
| Primer | 80 555 |
| Probed site | 11 532 |
| Quantitative Trait Locus, QTL | 11 625 |
| Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA, RAPD | 175 |
| Restriction fragment length polymorphism | 18 761 |
| Simple Sequence Repeat, SSR | 24 422 |
| Sequence Tagged Site, STS | 3437 |
| Telomere | 20 |
Marker types and number of records of each represented as data sets in the Gramene Markers biomart database
| Marker type/BioMart data set . | Number of records . |
|---|---|
| Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism, AFLP | 8150 |
| Breakpoint interval | 303 |
| Centromere | 57 |
| Clone | 2 242 577 |
| Deletion | 333 |
| EST cluster | 6 154 296 |
| Expressed sequence Tag, EST | 20 690 805 |
| Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization, FISH, Probes. | 37 |
| Fingerprint Contig, FPC | 17 479 |
| Genome Survey Sequence, GSS | 10 653 993 |
| Gene prediction | 354 564 |
| Gene | 10 781 |
| Genomic DNA | 5 263 129 |
| Insertion Site-Based Polymorphism, ISBP | 691 |
| Insertion | 310 |
| Microarray probe | 260 656 |
| mRNA | 651 207 |
| Overgo hybridization probe | 24 464 |
| Oligonucleotide | 2 396 466 |
| Point | 332 |
| Primer | 80 555 |
| Probed site | 11 532 |
| Quantitative Trait Locus, QTL | 11 625 |
| Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA, RAPD | 175 |
| Restriction fragment length polymorphism | 18 761 |
| Simple Sequence Repeat, SSR | 24 422 |
| Sequence Tagged Site, STS | 3437 |
| Telomere | 20 |
| Marker type/BioMart data set . | Number of records . |
|---|---|
| Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism, AFLP | 8150 |
| Breakpoint interval | 303 |
| Centromere | 57 |
| Clone | 2 242 577 |
| Deletion | 333 |
| EST cluster | 6 154 296 |
| Expressed sequence Tag, EST | 20 690 805 |
| Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization, FISH, Probes. | 37 |
| Fingerprint Contig, FPC | 17 479 |
| Genome Survey Sequence, GSS | 10 653 993 |
| Gene prediction | 354 564 |
| Gene | 10 781 |
| Genomic DNA | 5 263 129 |
| Insertion Site-Based Polymorphism, ISBP | 691 |
| Insertion | 310 |
| Microarray probe | 260 656 |
| mRNA | 651 207 |
| Overgo hybridization probe | 24 464 |
| Oligonucleotide | 2 396 466 |
| Point | 332 |
| Primer | 80 555 |
| Probed site | 11 532 |
| Quantitative Trait Locus, QTL | 11 625 |
| Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA, RAPD | 175 |
| Restriction fragment length polymorphism | 18 761 |
| Simple Sequence Repeat, SSR | 24 422 |
| Sequence Tagged Site, STS | 3437 |
| Telomere | 20 |
The Gramene Markers database allows users to filter by, and export attributes related to species, germplasm, name/synonym, library/source and related (corresponding) entities. An example query against the Gramene Markers database is included as ‘Query 3’ in Table 1.
Gramene Mappings database
The Gramene Mappings database models the mappings between markers (described above) and molecular maps. The various map types, bin, cytogenetic, deletion, genetic, physical, quantitative trait loci (QTL), sequence, are each modelled as a separate data set.
The Gramene Mappings database allows users to filter by, and export attributes related to species, map set/map (e.g. chromosome), map position, marker name, marker type and analysis. An example query against the Gramene Mappings database is included as ‘Query 4’ in Table 1.
Gramene QTL database
The QTL database contains details of all QTL in Gramene; currently 11 624 from 10 species. The focus of this database is querying and reporting QTL by Trait Ontology (22) term. An example query against the Gramene QTL database is included as ‘Query 5’ in Table 1.
Discussion and future directions
Gramene has been a long-standing user of the BioMart software. We have deployed both the Ensembl data transformation and interface configuration, and also developed Gramene-specific transformations from our MySQL-based data resources on custom schemas for which we made extensive use of the BioMart MartBuilder and MartEditor software. GrameneMart has become an integral and well-used component of the Gramene website. We will adopt software updates from both Ensembl and BioMart projects as appropriate.
Gramene's future BioMart efforts will be focused on data federation, both internally between Gramene databases, and externally with third-party data sets. We anticipate that this will significantly increase the utility of Gramene's extensive ontology and phenotypic linkage data.
Funding
National Science Foundation (NSF) (Grant numbers 0703908, 0851652). Funding for open access charge: NSF (Grant IOS-0703908).
Conflict of interest. None declared.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank our users for their feedback and support as well as our collaborators and contributors who have supplied Gramene with data. We would also like to thank the BioMart team at the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research (OICR) for developing and supporting the BioMart software, and also to the Ensembl and Ensembl Genomes teams at the European Bioinformatics Institute and Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute for developing and supporting the Ensembl software.



